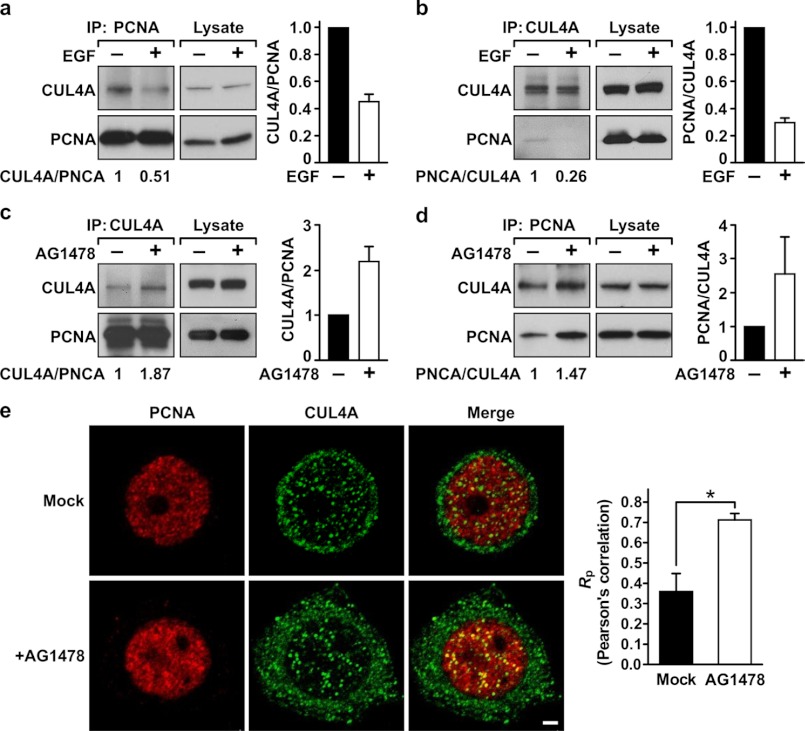
FIGURE 4.
Association between CUL4A and PCNA is negatively regulated by EGFR. A and B, MDA-MB-468 cells were serum-starved for 24 h and then stimulated by EGF (10 ng/ml) for 30 min. The cells were then lysed in NETN buffer and subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) by the indicated antibodies. Immunoprecipitated PCNA (A) or CUL4A (B) was examined for the level of associated CUL4A or PCNA, respectively. C and D, MDA-MB-468 cells grown in normal conditions were treated with the EGFR kinase inhibitor AG1478 for 6 h. The cells were lysed, and the lysate was then subjected to immunoprecipitation for PCNA (C) or CUL4A (D). The associated CUL4A and PCNA was then assessed by Western blotting analysis. Average binding activities between these two proteins from two independent experiments are shown. E, MDA-MB-468 cells grown in normal condition were mock-treated or treated with AG1478 as described in C and then stained with primary antibodies against PCNA or CUL4A. Secondary antibodies conjugated with rhodamine and FITC were used to detect PCNA (red) and CUL4A (green), respectively. The slides were examined by fluorescence confocal microscopy, with photosections of 0.48 μm each. Note that in the merged images, colocalization of PCNA and CUL4A appears as yellow in the nucleus. Nuclear colocalization of PCNA and CUL4A was quantitated using the ImageJ program. Right, Pearson's correlation coefficients (Rp) are shown. A coefficient of +1 indicates complete colocalization. For details, see under “Experimental Procedures.” Error bars, S.E. *, p < 0.05.