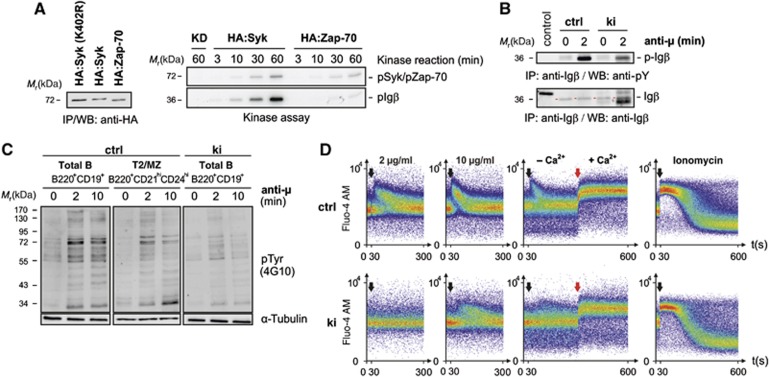
Figure 3.
Reduced Syk-family kinase activity in Sykki cells translates into attenuated anti-IgM-induced phosphotyrosine signalling and a diminished B lymphocytic Ca2+ response. (A, left) To compare their auto- and transphosphorylation capacity, HA:Syk and HA:Zap-70 were stably expressed in CHO cells at comparable, low levels as shown by anti-HA immunoprecipitation (IP) and western blotting (WB). A kinase-dead mutant (KD) of Syk, HA:Syk(K402R) served as negative control. Associated kinase activity was assayed by incubation of a part of the anti-HA immunoprecipitated material in vitro in the presence of Mg2+, γ-ATP-32P and recombinant GST-Igβ (A, right) for the indicated time points. (B) To assess the phosphorylation state of Igβ in vivo, splenic B cells from Sykwt and Sykki mice were left untreated (0) or stimulated with anti-IgM (anti-μ) for 2 min; subsequently, Igβ (red arrows) was immunoprecipitated and the amount of total Igβ and p-Igβ (4G10) was determined. (C) Phosphotyrosine levels (4G10) of total ctrl (B220+CD19+), T2/MZ ctrl (B220+CD21hiCD24hi) and total ki (B220+CD19+) B cell lysates after anti-IgM F(ab′)2-mediated stimulation. (D) Reduced anti-IgM-induced calcium responses of fluo-4 AM-loaded splenic B220+CD19+ ki B cells; black arrows indicate the addition of anti-IgM at concentrations depicted above response curves; red arrows mark the addition of extracellular Ca2+ (1.5 mM) to measure the store-operated calcium entry after depleting ER stores with anti-IgM (10 μg/ml); ionomycin was used as a positive control. Each figure is representative for three independent experimental repeats; KD, kinase-dead. ctrl, control; Ig, immunoglobulin. Figure source data can be found with the Supplementary data.