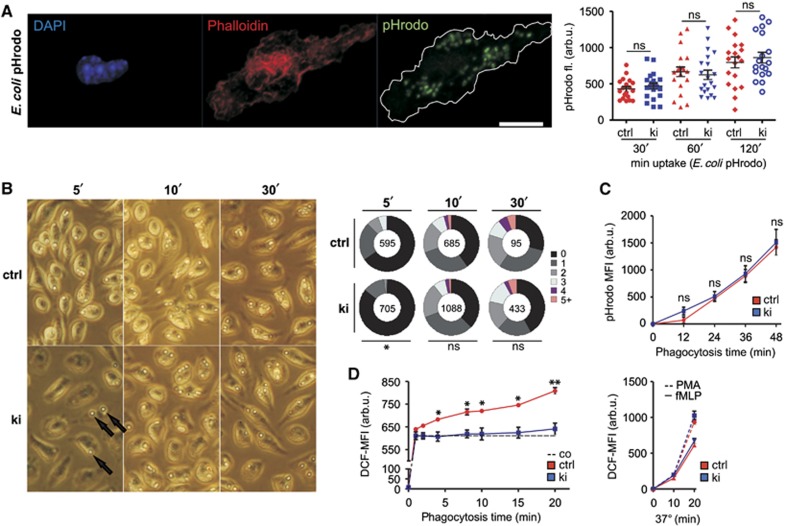
Figure 5.
Differential requirements of Syk-family kinase activity for macrophage or polymorphonuclear neutrophil FcγR-mediated immune complex phagocytosis versus reactive oxygen species production. (A) Bone marrow-derived macrophages and (C) polymorphonuclear cells were incubated with E. coli particles to compare scavenger receptor-mediated uptake kinetics between ctrl and ki cells, delineating the functionality of non-ITAM-bearing receptors. (A, left) Representative image of a ctrl macrophage triple stained for the nucleus (4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole, DAPI), F-actin (Phalloidin) and internalized pHrodo particles; scale bar=10 μm. (A, right) Integrated pHrodo fluorescence determined within the F-actin+ footprint of 20 macrophages for each condition 30, 60 and 120 min after particle addition. (B) To assess FcγR-mediated phagocytosis in macrophages, sheep erythrocytes (arrows) were opsonized with anti-hemolysin antibodies and incubated with macrophages for 5, 10 and 30 min at 37°C; pie charts indicate percentages of macrophages having internalized 0 to 5+ SRBCs, and numbers in the centre indicate the total number of macrophages analysed per condition. (C) Uptake of pHrodo E. coli particles by PMNs showed that proper Syk kinase activity was also dispensable for scavenger receptor-mediated phagocytosis in PMNs. (D, left) IgG-BSA-H2DCF immune complex-induced ROS production was severely compromised in Sykki PMNs, whereas fMLP (10−6 M) and PMA (10−7 M) elicited comparable responses (D, right), indicating selective ablation of FcγR-mediated signalling. *P<0.05, **P<0.01; n=3 (B–D). arb.u., arbitrary units; co, control (on ice); ctrl, control; DCF, dichlorofluorescein; ns, not significant; PMA, phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate.