Figure 1.
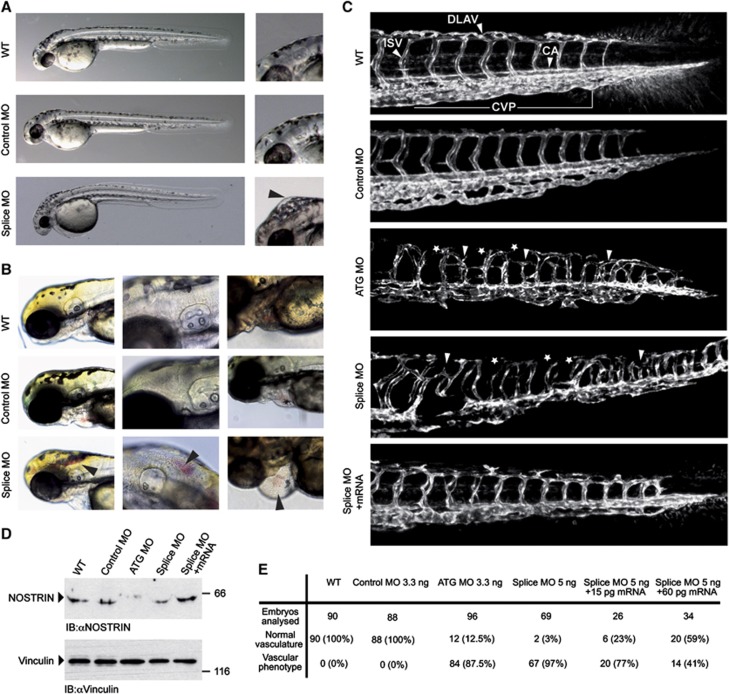
MO-mediated KD of NOSTRIN in developing zebrafish embryos causes vascular defects. Tg(fli1a:EGFP)y1 zebrafish embryos were injected with 3.3 ng Control MO, 3.3 ng ATG MO, 5 ng Splice MO or 15 pg zebrafish NOSTRIN mRNA, if not indicated otherwise. All zebrafish images are lateral views with the anterior to the left and the dorsal side up. (A) Development of NOSTRIN morphants. Embryos injected with the Splice MO showed an overall regular development at 48 hpf when compared to WT embryos or embryos injected with Control MO (left). Higher magnification of embryo heads, black arrowhead pointing to hindbrain oedema in embryo injected with the Splice MO (right). (B) Cranial haemorrhaging (left and middle) and pericardial oedema and haemorrhaging (right) in embryos injected with the Splice MO analysed at 72 hpf, black arrowheads indicating red blood cells. (C) CLSM images of trunk regions taken at 48 hpf, with the vascular structures visualised by eGFP fluorescence and labelled ISV (intersegmental vessel), CA (caudal artery), DLAV (dorsal longitudinal anastomotic vessel) and CVP (caudal vein plexus) showed regular development in the WT and embryo injected with Control MO. In embryos injected with the ATG or Splice MO false connections between neighbouring ISVs were formed (indicated by white arrow heads), the DLAV was interrupted (indicated by asterisks) and the caudal vein plexus was irregular in appearance in both morphants. Co-injection of NOSTRIN mRNA with the Splice MO almost completely re-established the ISV trajectory, DLAV integrity and CVP regularity. (D) The efficient KD of NOSTRIN after injection of ATG MO or Splice MO and the expression of NOSTRIN after mRNA co-injection were verified by immunoblotting of whole fish lysates prepared at 48 hpf using a NOSTRIN-specific antiserum, an immunoblot of vinculin demonstrated loading of equal amounts. (E) Quantitative analysis of live embryos at 48 hpf treated as indicated; vascular phenotype included abnormal ISV trajectory, DLAV discontinuity, oedema, haemorrhaging.