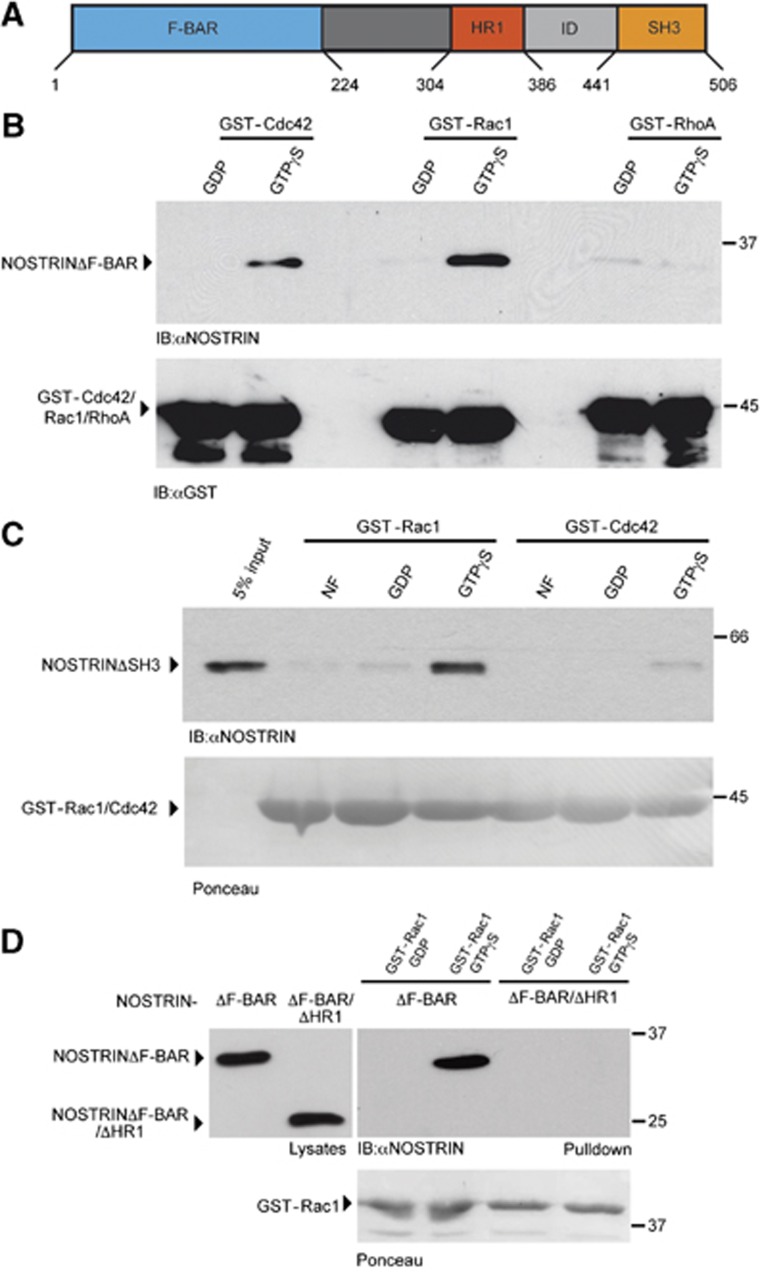
Figure 4.
NOSTRIN interacts with Rac1 via the HR1 motif. (A) Domain structure of NOSTRIN. Amino acid numbers indicate the N- and C-terminal borders of the F-BAR, HR1, ID (intermediate domain) and SH3 domains. (B) NOSTRIN interacts with Rac1. GDP- or GTPγS-loaded GST-Cdc42, GST-Rac1 and GST-RhoA were used for GST-pulldown experiments using cell lysates expressing NOSTRIN. NOSTRIN (NOSTRINΔF-BAR) interacted specifically with GTPγS-loaded GST-Rac1 and to a lesser extent with GTPγS-loaded GST-Cdc42, while it did not interact with RhoA, independent of the nucleotide bound. (C) NOSTRIN interacts directly with active Rac1. Nucleotide free (NF), GDP- or GTPγS-loaded GST-Rac1 or GST-Cdc42 were used for GST-pulldown experiments in combination with purified recombinant NOSTRINΔSH3. 5% of the amount of purified NOSTRINΔSH3 used for GST-pulldown is shown for comparison of protein levels (5% input). NOSTRIN (NOSTRINΔSH3) interacted strongly and directly with GTPγS-loaded GST-Rac1. (D) NOSTRIN interacts with Rac1 via the HR1 motif. GDP- or GTPγS-loaded GST-Rac1 was used for GST-pulldown experiments using cell lysates expressing NOSTRINΔF-BAR and NOSTRINΔF-BAR/ΔHR1. Immunoblot from cell lysates shows expression of equal amounts of NOSTRINΔF-BAR and NOSTRINΔF-BAR/ΔHR1 (left). In the GST-Rac1 pulldown GTPγS-loaded GST-Rac1 interacted specifically with NOSTRINΔF-BAR, but not with NOSTRINΔF-BAR/ΔHR1 (right). (B–D) NOSTRIN was detected by immunoblotting with NOSTRIN-specific antibody (Mookerjee et al, 2007). Equal amounts of GST-Rac1, GST-Cdc42 or GST-RhoA, respectively, were used, detected by immunoblotting with a GST-specific antibody or Ponceau staining, as indicated.