Figure 5. Septation of the truncus arteriosus.
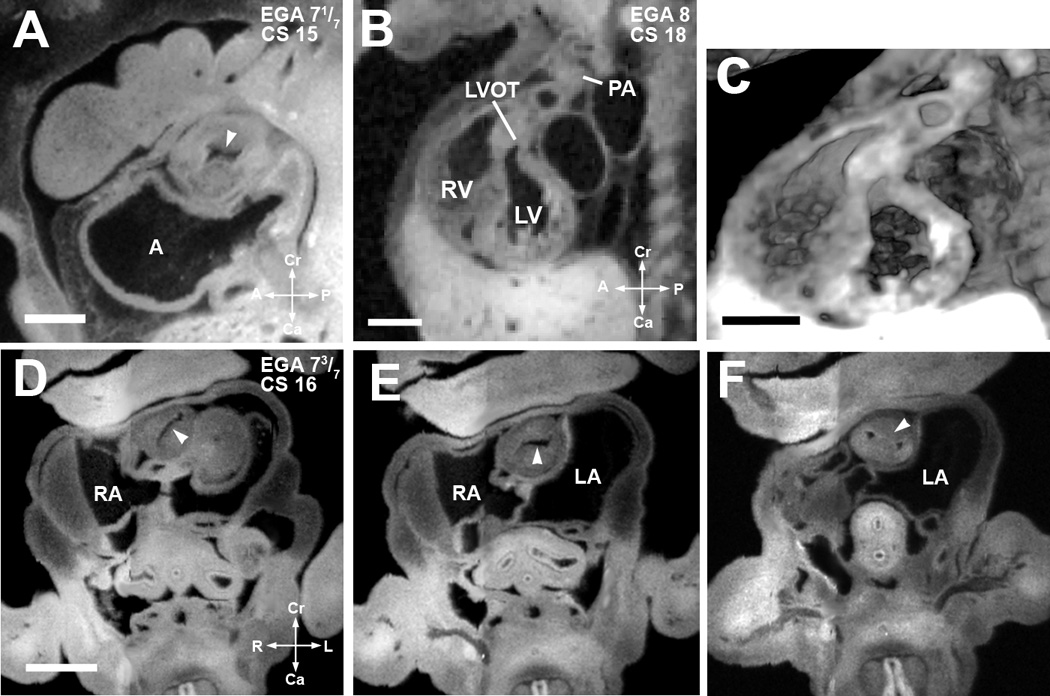
(A). EFIC image of an embryo at EGA 7 1/7 weeks (CS 15) in the sagittal plane shows a single orifice of the truncus arteriosus with inward swelling of the aorticopulmonary septum (arrowhead) which precedes septation of the truncus arteriosus. Scale bar = 0.622 mm.
(B,C) EFIC image of an EGA 8 (CS 18) embryo (B) show a distinct pulmonary artery (PA) emerging from the right ventricle (RV) and a left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) or aorta emerging from the left ventricle (LV). 3D volume of the same embryo (C) shows crossing of the great arteries. Scale bar in (B,C)=1.35 mm.
(D–F). EFIC images of a embryo at EGA 7 3/7 weeks (CS 16) in oblique transverse planes showing the truncus arteriosus. Note changing orientation of the lumen (D,E) indicative of spiraling of the cushions (see arrowheads). In (F), the aorticopulmonary septum (arrowhead) has divided the distal portion of the truncus arteriosus into two separate arterial channels to the right and left of the aorticopulmonary septum. Scale bar = 0.9 mm.
A: primitive atrium, RA: right atrium, LA: left atrium, RV: right venetricle, LV: left ventricle.
