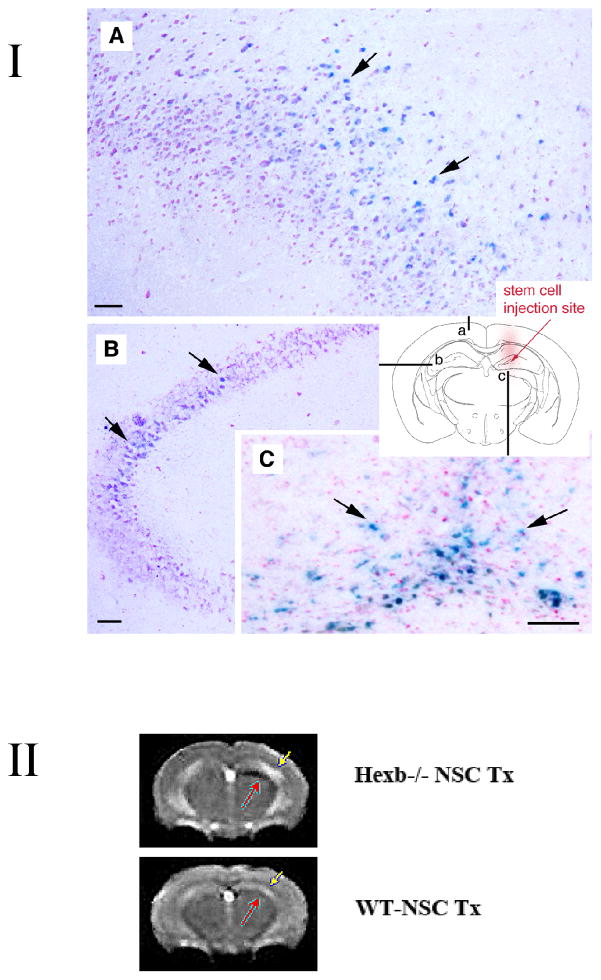
Figure 1.
I. NSC transplants survive and engraft in Sandhoff disease Hexb−/− mouse model. Adult symptomatic mice 12–13 weeks of age were used. Using a stereotaxic frame (KOPF®), through a 0.9-mm diameter hole in the skull (2-mm posterior to bregma; 1.5-mm lateral to sagittal suture), 4 μl (8 × 104 cells/μl) of C17.2 cells in PBS was injected unilaterally into the hippocampus (right hemisphere) under isofluorane anaesthesia. Mock-grafted controls received the same volume of PBS. Coronal brain sections were permeabilized with detergents and exposed to a chromogenic substrate X-gal to detect β-gal-labeled donor cells. The blue cells (X-gal histochemical reaction, arrows) have engrafted in the recipient brain with widespread migration, distribution, and integration. Representative images of the brain (A–C) from 15-week-old Hexb−/− mice are shown (n=7). Schematic diagram (a–c) illustrates where images are from (images A–C, respectively) in relation to injection site. Scale bar = 10 μm. Counter stain = neutral red.
II. Noninvasive MRI tracking of neural stem cells in live mice. T2-weighted image acquired with a fast spin-echo sequence (TR=3s, TE=48ms), 1-mm coronal slice with an in-plane resolution of 234 μm, at posttransplantation day 38. Injection site of Sinerem®-labeled stem cells is clearly visible (red arrow) in the right hemisphere of Hexb−/− mice, while minimal change in signal intensity is evident in the wild-type transplanted mice which had received the same number of Sinerem®-labeled stem cells. More NSCs (black, red arrow) are located juxtaposed to T2 hyperintensity in the cortex (yellow arrow, which could represent increased inflammation) compared to similarly transplanted NSCs in wild type mice, which show no such T2 signal (yellow arrow) & very few, if any, NSCs (black, red arrow) accumulating in the cortex). Although the main migration streams were detected with MR, the technique does not have the sensitivity to detect lower cell densities readily detected histologically. n=2 per group.