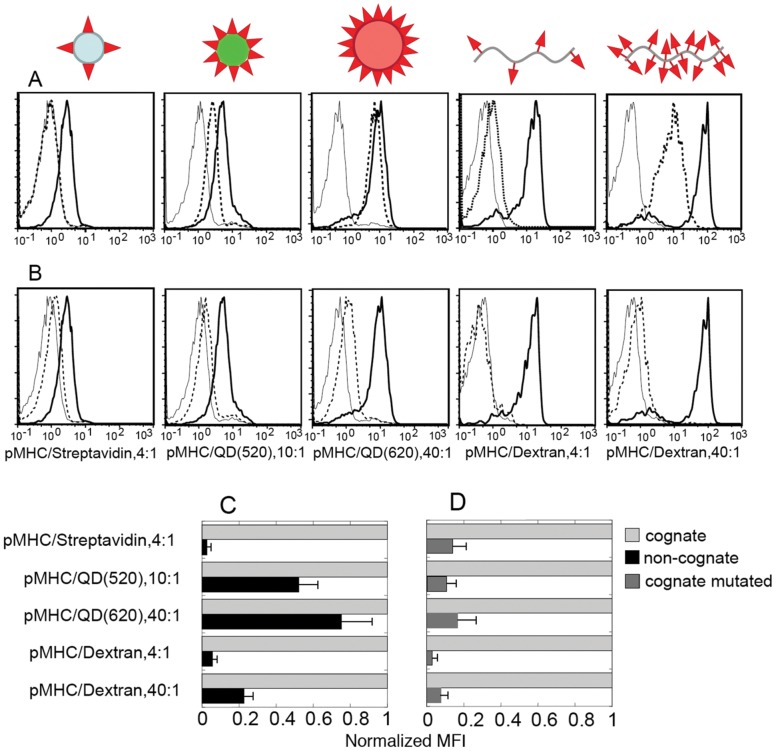
Figure 2. Comparison of the binding of various cognate and noncognate pMHC oligomers to CD8 CTL. A.
Binding of cognate (IV9-HLA-A2, bold solid line) and noncognate (Tax-HLA-A2, dotted line) pMHC ligands assembled on different scaffolds to 68A62 CTL as established by flow cytometry. The CTL were incubated with each oligomer at 20 nM for 30 min prior to the analysis. Mutant HLA-A2(A245V) loaded with noncognate peptide (Tax) was used to produced oligomers which were utilized as negative controls (solid line). B. Binding of different oligomers carrying cognate peptide (IV9) in association with either intact (bold solid line) of mutated HLA-A2 (A245V) (dashed line) to 68A62 CTL was evaluated. Binding of cognate dextramers in the presence (dashed) or absence (bold solid line) of blocking anti-CD8 antibodies was examined. Other conditions are as in A. Data represent mean ± s.d. C. Normalized MFI of 68A62 bound to cognate or noncognate pMHC oligomers containing intact HLA-A2 protein. The nature of oligomers and the number of pMHC ligands per oligomer are indicated. Data represent mean ± s.d. D. Normalized MFI of 68A62 bound to cognate oligomers or cognate oligomers containing pMHCmut with mutated HLA-A2 (A245V) protein. The tested oligomers are as in C.