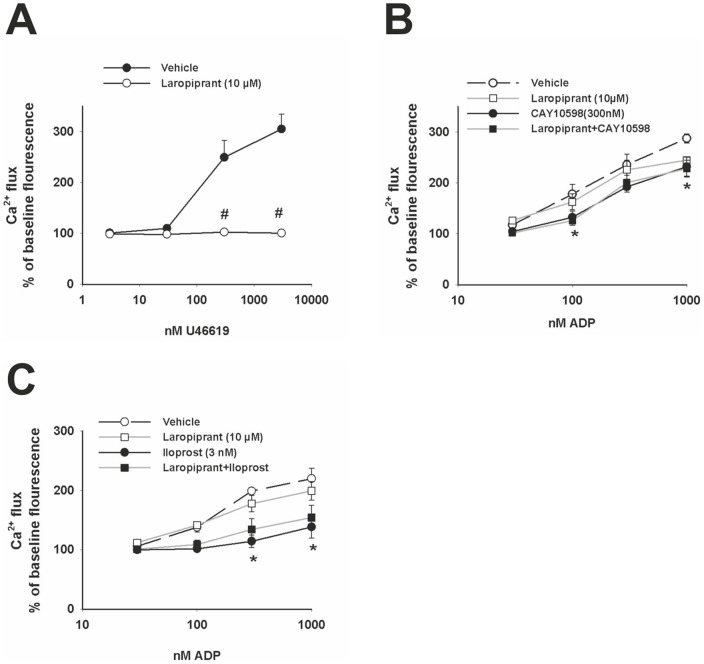
Figure 4. Laropiprant antagonizes Ca2+ mobilization induced by TP receptor activation.
Ca2+ responses were detected by flow cytometry as changes in fluorescence of the Ca2+ -sensitive dye Fluo-3 by flow cytometry and are presented as percent of baseline fluorescence. (A) The TP agonist, U46619 (3–3000 nmol/L), induced Ca2+flux in a concentration-dependent manner and this effect was completely inhibited by laropiprant at 10 μmol/L (n = 6). (B) The EP4 receptor agonist CAY10598 (300 nmol/L) and (C) the IP receptor agonist iloprost (3 nmol/L) caused a significant inhibition of the ADP-induced Ca2+ flux (n = 4). Laropiprant (10 µmol/L) did not antagonize these effects (n = 4). Values are shown as mean+SEM. *P<0.05 as compared to vehicle and #P<0.05 as compared to the respective agonist treatment treatment.