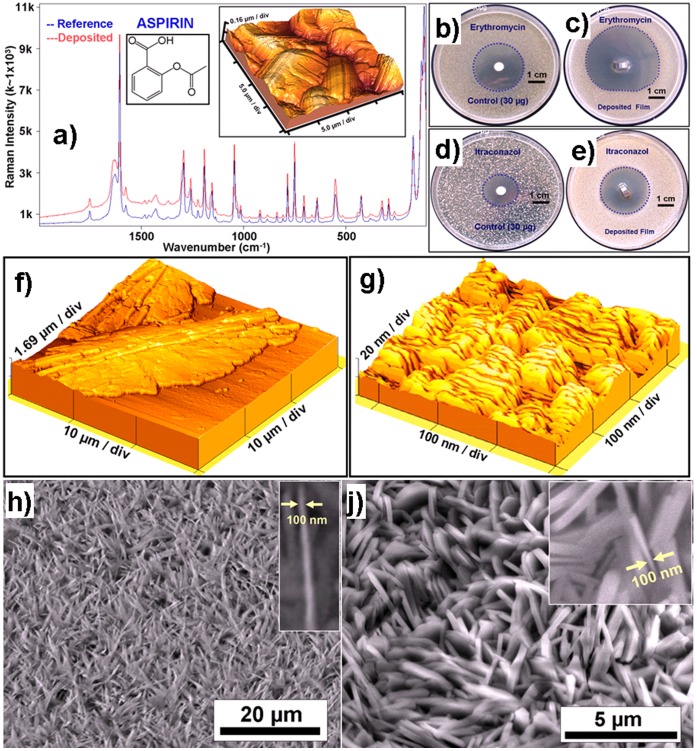
Figure 1. Analysis of TE deposited pharmaceutical films on Ti-substrates.
a) Raman spectra of the deposited and reference acetyl salicylic acid (ASS), showing clear Raman peaks in the TE deposited ASS. 3D AFM image in the figure a, from the TE ASS sample, shows the micro-crystallites of ASS. b–e: The antimicrobial activity of Erythromycin (b: control, c: TE deposited) against Staphylococcus aureus and of Itraconazole (d: control, e: TE deposited) against Candida albicans demonstrated in agar diffusion tests. The activity is significantly increased in the case of specimen deposited by TE. f) Tuneable crystallinity: 3D Atomic force microscope image of Nipasol grown on Ti substrate at room temperature resulting in a much larger crystal size as compared to that deposited at −100°C as shown in g) which is nano-crystalline. h) & j) SEM images of nanostructured Cholesterol h) and Tetracaine-HCl j) drugs respectively fabricated on different substrates by thermal evaporation showing nanoscale spikes, see insets. The nanospike or platelet like geometries result from the growth kinetics.