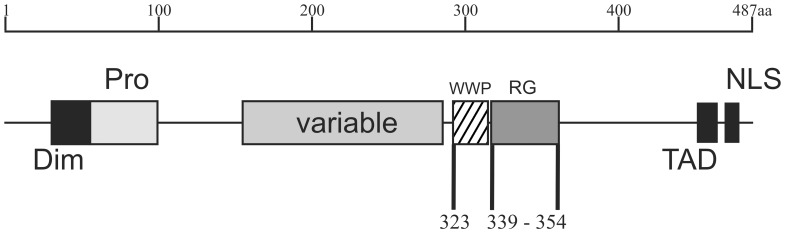
Figure 1. Schematic representation of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 (EBNA2).
EBNA2 of the standard B95.8 strain (accession number: AJ507799) of EBV consists of 487 amino acids (aa) present in an A-type virus. The N-terminal dimerization domain (“Dim”) is located next to a poly-Proline stretch (“Pro”). The variable region (“variable”) differs between the A-type viruses and B-type viruses. B-type viruses have a reduced in vitro transformation potential. The binding site for RBPjκ (“WWP”) is located around a Trp-Trp-Pro motif at aa 323–325. The adjacent Arginine-Glycine repeat (“RG”) between aa 339–354 confers binding to the survival of motor neurons (SMN) protein and represents the second nuclear localization signal (“NLS”) in addition to the canonical NLS found at the extreme C-terminus between aa 468–487. The C-terminal acidic transactivation domain (“TAD”) between aa 424–468 interacts with various basal transcription factors.