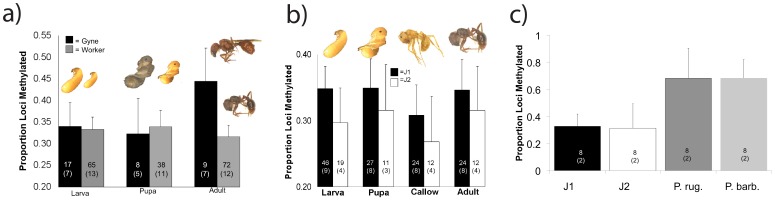
Figure 3. Global trends of CpG methylation.
a) The proportion of methylated loci increases in queens in adulthood, but is constant for workers over development. Only adult workers and virgin queens differed, with virgin queens having significantly more methylated DNA (P<0.05). In b) variation in the proportion of methylated loci between workers of different hybrid origin. Labels indicate the maternal lineage; all workers are hybrids between the J1 and J2 lineages. The direction of hybridization affected the degree of methylation, with workers from J1 mothers and J2 fathers being 17% more methylated (P<0.05) than those from the reciprocal cross. In c) a comparison between four lineages: P. barbatus and P. rugosus have normal (environmental) caste determination and ancestrally hybridized to give rise to the J lineages (which have genetic caste determination). The J lineages are significantly less methylated (P<0.05) than their parental species. Together, b) and c) show that two successive rounds of hybridization both changed the degree of genome methylation present in workers. All error bars are 95% C.I. Numbers inside the bars indicate sample sizes, and the number of colonies from which individuals were sampled (in parentheses).