Figure 7.
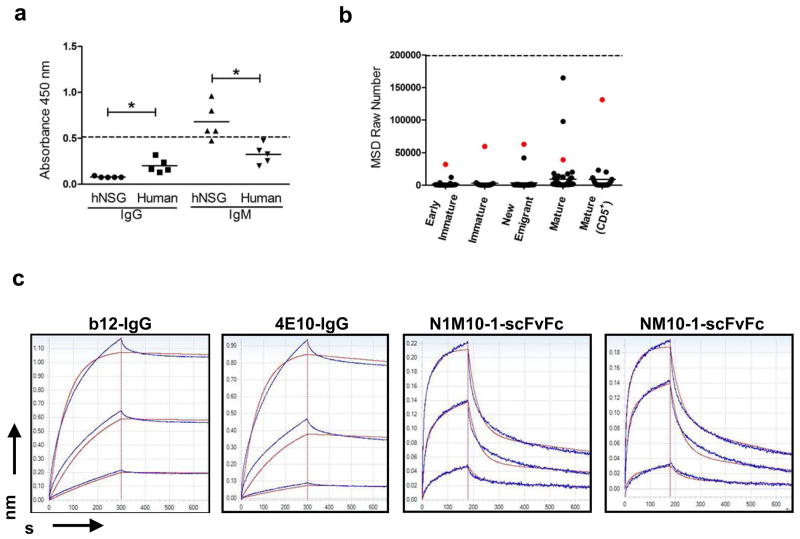
Binding of hNSG Abs to recombinant HIV-1gp140. (a) Sera from 5 hNSG mice and 5 normal human subjects were tested by ELISA for binding to recombinant HIV-1gp140 coated at a concentration of 5 μg/ml per well. Each serum sample was tested in two sets of duplicates, each set scored for human IgM or IgG (x-axis) mediated antigen as described previously (see Figure 5). All serum samples were used at 1:100 dilution. The horizontal dashed line represent the level of reactivity by 4E10 IgG (5 μg/ml) used as a positive control. Significant differences in reactivity between data sets as indicated (*p<0.005) was calculated using the Mann-Whitney unpaired t-test. (b) HIV-1gp140 reactivity of the scFvFcs isolated from the different B cell subsets (indicated on the x-axis) was tested using the MSD platform. HIV envelope protein was coated at a concentration of 5 μg/ml per well. All samples were tested in duplicates, and the mean value in MSD raw numbers (y-axis) as obtained in the MSD Sector Imager was plotted. 4E10 scFvFc was used as positive control (represented as the horizontal dashed line), and readings obtained with PBS binding to antigen coated wells was considered as background. Each dot represents the binding of an individual scFvFcs, and the horizontal bar represents mean reactivity for each cell subset. The same scFvFcs in each B cell subset has been color coded (red dot) as in Figure 6. Reactivity to HIV-1gp140 was significantly higher in the mature B cell subsets (median reactivity in Mature vs. Early immature/Immature/New emigrant and Mature CD5+ vs. Early immature/Immature/New emigrant, p<0.005). Differences in median reactivity between the scFvFcs of each B cell subset were calculated using the Mann-Whitney unpaired t-test. (c) Affinity measurements of the hNSG derived scFvFcs to HIV-1gp140 were obtained using Biolayer interferometry. Representative sensorgrams of two HIV BnABs (b12-IgG and 4E10-IgG) and two randomly selected polyreactive scFvFcs (NM10-1 and N1M10-1, color coded in Figure 6) binding to different concentrations of recombinant HIVgp140 trimer are shown. Antibodies were loaded on Protein A sensors which were dipped into recombinant HIVgp140 in solution to determine association followed by dissociation in PBS. Traces were obtained for antibody binding to a range of HIVgp140 trimer concentrations. Dissociation was performed for up to 1800 s, but steady state was attained by 600 s which is shown here. Binding responses to <10 nM HIV envelope protein were negative in case of the scFvFcs; therefore only the binding traces obtained for 50 nM and 16.6 nM and 5.6 nM of HIVgp140 are shown. Experiments were repeated at least three times with different lots of proteins. Affinity measurement values for each antibody are described in Results.