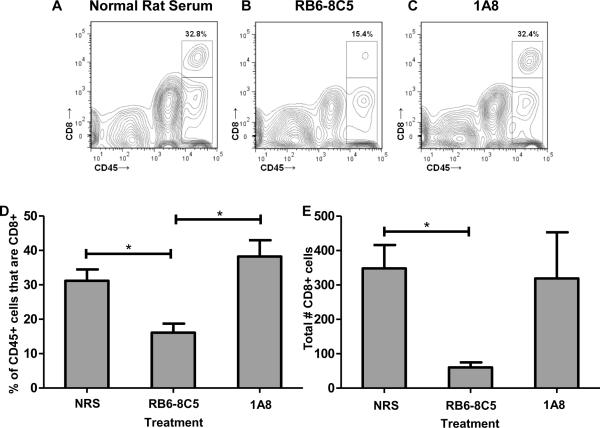
Figure 3. The anti-granulocyte receptor-1 (GR-1) mAb RB6-8C5 depletes CNS-infiltrating CD8+ cells in mice administered VP2121-130 peptide to induce PIFS.
Representative contour plots showing the effect of treatment with (A) normal rat serum, (B) RB6-8C5, and (C) 1A8 on the percentage of CD45+ cells that are also CD8+. (D) The CD45hi population was gated and analyzed for the percentage of CD8+ cells in each of the three treatment groups (n=6 per group). RB6-8C5-treated mice demonstrated a significant reduction in brain-infiltrating CD8+ cells as a percentage of CD45+ cells when compared to those treated with normal rat serum (p<0.05) or 1A8 (p<0.05). There was no significant difference between treatment with normal rat serum and treatment with 1A8 (p=0.386). (E) Treatment with RB6-8C5 also significantly reduced the total number of CD8+ cells when compared to treatment with normal rat serum (p<0.05). Significance between groups was determined by an ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple comparison test. Error bars indicate SEM. Shown are the results of one experiment representative of two.