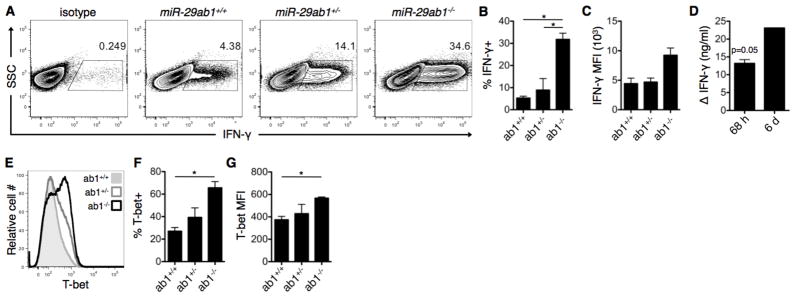
Figure 2. miR-29 derived from the miR-29ab1 genomic cluster is necessary to restrain Th1 programming.
(A) CD4+ T cells were purified from miR-29ab1 wild-type (ab1+/+), heterozygote (ab1+/−), and knockout (ab1−/−) mice, and activated under ThN conditions with no exogenous cytokines/neutralizing antibodies. IFN-γ expression was assessed on day 6 of culture by intracellular flow cytometry. (B–D) Additional quantification of IFN-γ expression following activation as in (A), including (B) percentage of IFN-γ-expressing cells, (C) mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of IFN-γ+ cells, and (D) IFN-γ concentration in culture supernatants of knockout relative to wild-type cultures at 68 h and 6 d post-culture. Data are representative of two independent experiments and values are means ± SEM. *p<0.05; ANOVA Tukey’s post-hoc test (B–C) or Student’s one-sample t-test (D). (E) T-bet expression was assessed in T cell cultures from (A) using intracellular flow cytometry. (F–G) Additional quantification of T-bet expression including (F) percentage of T-bet-expressing cells and (G) MFI of T-bet+ cells. Data are representative of two independent experiments and values are means ± SEM. *p<0.05; ANOVA Tukey’s post-hoc test.