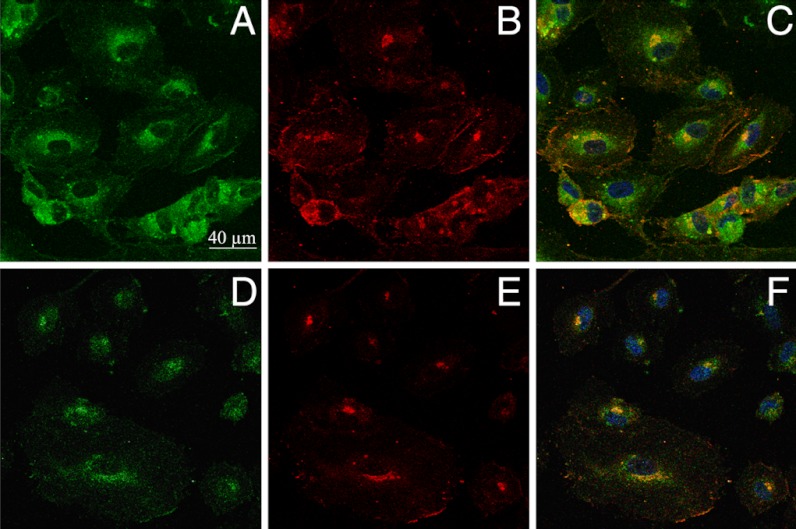
Fig. 5.
Colocalization imaging of NS1 and eNOS. Living HUVECs were treated with NS1 (10 μM) for 60 min prior to fixation and immunostaining of eNOS. Primary and secondary antibodies for immunostaining were purified mouse anti-eNOS/NOS Type III and AlexaFluor 594 goat anti-mouse IgG (H + L), respectively. (A and D) Imaging channel of NS1 [1-PE (488 nm) and 2-PE (840 nm), respectively; emission at 520–680 nm]; (B and E) imaging channel of eNOS (1-PE, 543 nm; emission at 590–700 nm), corresponding to A and D, respectively; (C) merged image of A and B; (F) merged image of D and E. Yellow to orange areas indicate colocalization of NS1 and eNOS. Nucleus staining by Hoechst 3342 is also shown in C and F. Upon prolonged incubations (1–3 h) with NS1 (1–10 μM), the cells did not modify their shapes without fading of NS1signal upon 1-PE and 2-PE.