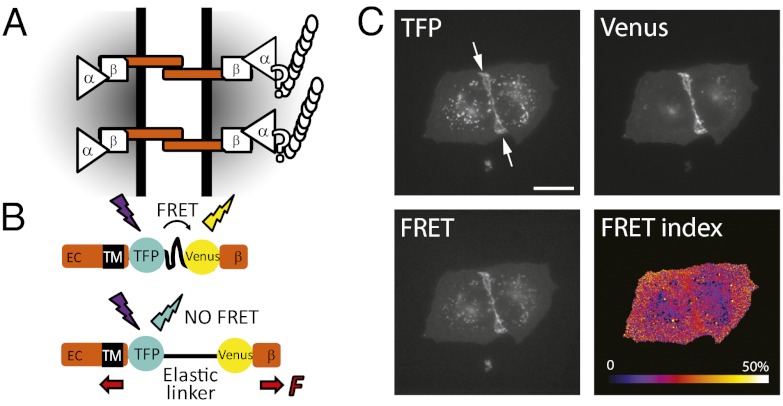
Fig. 1.
(A) Working model for mechanotransduction through the E-cadherin/catenin complex. E-cadherin transmits mechanical tension between cells via transinteracting extracellular (EC) domains and to the actin cytoskeleton through β-catenin, αΕ-catenin, and possibly other proteins. (B) The tension sensitive module (TSMod) consists of the mTFP/Venus FRET pair separated by an elastic linker (GPGGA)8 derived from spider silk. TSMod was inserted into the cytoplasmic domain of E-cadherin, where it can sense forces transmitted between the transmembrane domain (TM) and the β-catenin-binding domain (β). High and low FRET indices correspond to low and high tension, respectively. (C) Fluorescence imaging of two adherent MDCK cells expressing the EcadTSMod construct in the mTFP, Venus, and FRET (mTFP excitation; Venus emission) channels, and the corresponding map of FRET index = IFRET/(IFRET + ImTFP), where I is the fluorescence intensity of the subscript channel corrected for background and spectral bleed-through. (Scale bar: 20 μm.)