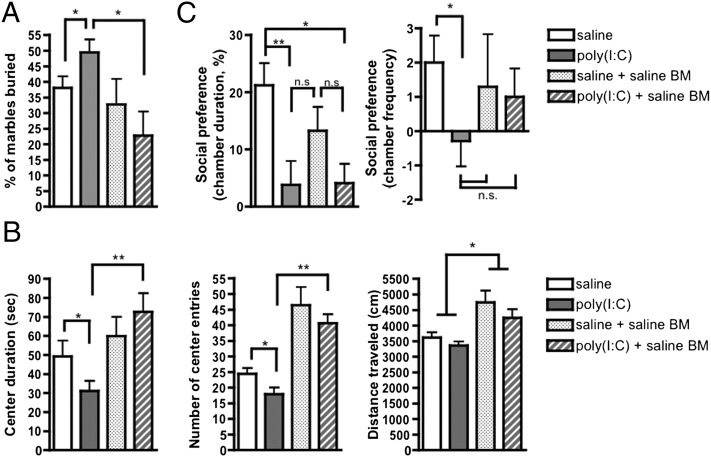
Fig. 4.
MIA offspring irradiated and transplanted with saline BM exhibit decreased repetitive and anxiety-like behavior. (A) Irradiation and transplantation of saline BM into MIA offspring restores repetitive marble-burying behavior to a level at or below that observed in controls. (B) Irradiation and transplantation of saline BM into MIA offspring decreases anxiety-like behavior as measured by significant increases in the number of center entries (Center) and duration in the center arena (Left), compared with those observed in untransplanted MIA mice. Both saline and poly(I:C) BM-transplant mice also exhibit increased overall activity in the open field, as measured by significantly increased total distance traveled compared with untransplanted mice (Right). (C) Transplanting saline offspring BM into poly(I:C) offspring has no significant effect on their social preference behavior, as measured by chamber duration (Left). There is, however, a trending improvement in social preference behavior as measured by chamber frequency in BM-transplanted MIA offspring (Right). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; n.s., not significant. BM-transplant data were acquired from one large experiment.