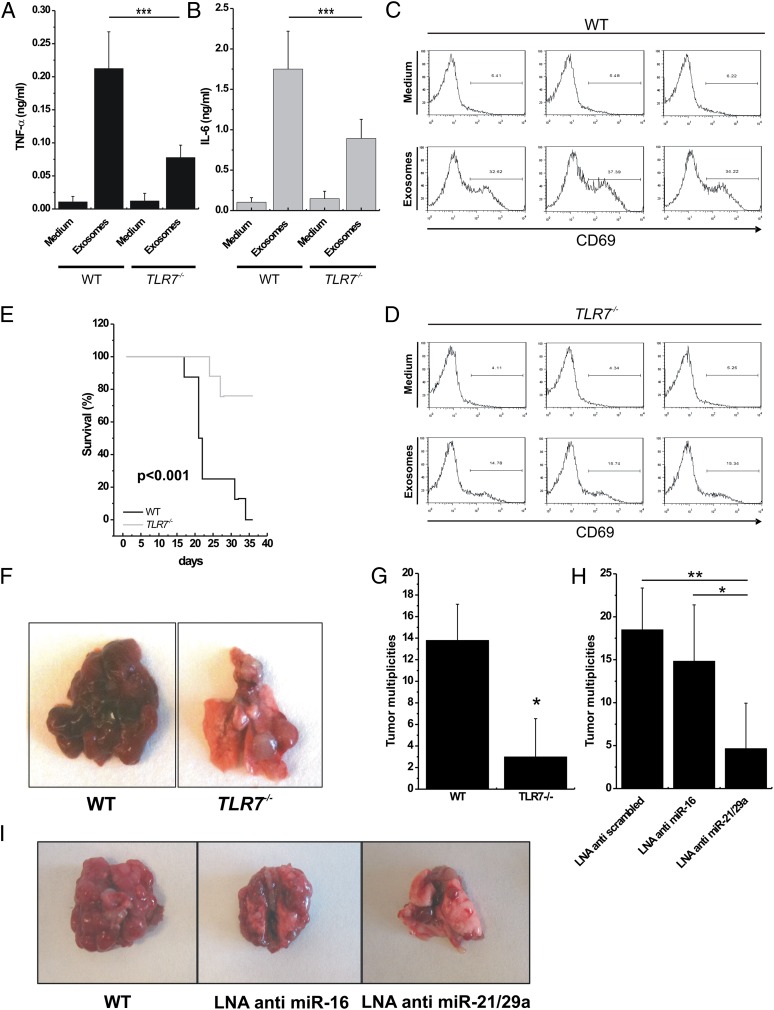
Fig. 4.
miRNA-induced TLR7 activation increases formation of lung multiplicities in mice. (A and B) ELISA for TNFα (A) and IL-6 (B) performed on conditioned medium of peritoneal macrophages isolated from WT (n = 3) and TLR7−/− (n = 3) mice, incubated with RPMI (Medium; negative control) or exosomes purified from LLC cells for 48 h. (C and D) Flow-cytometric analysis of CD69 in spleen cells isolated from WT and TLR7−/− mice treated as in A and B. (E) Kaplan–Meier curves for WT (n = 7) and TLR7−/− (n = 7) mice after tail injection of LLC cells. (F) Representative images of different tumor multiplicities detected in lungs in the WT and the TLR7−/− mouse groups. (G) Tumor multiplicities in the WT and TLR7−/− mouse groups, after tail injection of LLC cells. (H) Tumor multiplicities in B6 mice injected with LLC cells transfected with LNA anti-scrambled (control; n = 6), LNA anti–miR-16 (n = 6), or LNA anti–miR-21/29a (n = 6). (I) Representative images of lungs in mice injected with LLC cells transfected as indicated. Results in A–E, G, and H are shown as means ± SD. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.005.