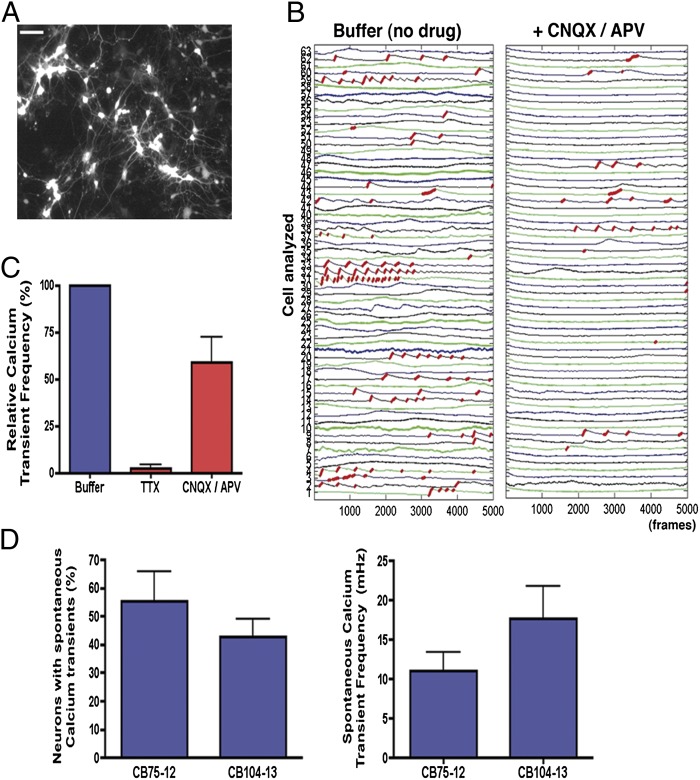
Fig. 3.
Activity-dependent calcium transients in CB-derived neurons. (A) Representative example of Syn::DsRed cultures of CB-derived mature neurons used for calcium signal traces. (Scale bar, 50 μm.) (B) Red traces correspond to the calcium rise phase detected by the algorithm used (SI Materials and Methods). Example of fluorescence intensity changes reflecting intracellular calcium fluctuations in CB-derived neurons before and after glutamate receptor antagonist (CNQX/APV) treatment. Each number on the left corresponds to the tracing of a different neuron on the plate. (C) Effects of TTX (1 μM) and CNQX/APV (10 μM/20 μM) on intracellular calcium transient frequency of individual neurons analyzed simultaneously by calcium imaging. (D) Analysis of spontaneous intracellular calcium transients in CB-derived neurons after 4 wk of differentiation. CB-derived neurons differentiated from two distinct CB-iNCs showed similar prevalence of calcium signaling as well as similar transient frequency within the neuronal population. Data shown as mean ± SEM.