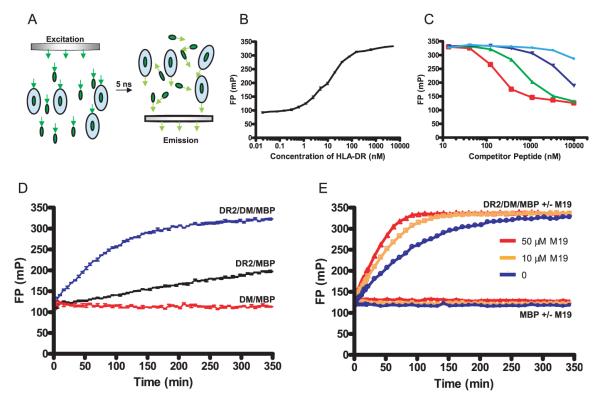
FIGURE 1.
Identification of small molecules that accelerate DM-catalyzed peptide exchange using a FP-based peptide binding assay. A, Principle of monitoring the binding of a fluorescently labeled peptide to DR by FP. The rate at which molecules tumble in solution is directly related to their molecular mass, and a small fluorescently labeled peptide tumbles significantly faster than the complex of such a peptide bound to a DR molecule. The light used for excitation of the fluorophore passes through a polarization filter (left), and the fraction of the emitted fluorescence that has retained polarization is measured following a 5-nanosecond delay (right). The relative intensities of polarized vs scattered emission depend on the ratio of DR-bound vs free fluorescent peptide. B, Analysis of peptide binding to DR2 by FP. An Alexa-488-labeled MBP peptide (10 nM) was incubated with DR2/CLIP at a wide range of concentrations (ranging from 20 nM to 5000 nM) overnight at 37°C. Free peptide yielded FP values of ~100 mA; FP values increased to ~320 mA when the majority of fluorescent peptide molecules were bound to DR2. Reactions were set up in triplicates, and the average and SDs are shown. FP was plotted as millipolarization units (mP), with larger numbers indicating that a larger fraction of emitted fluorescence has retained polarization. C, FP binding measurements are specific. Competitor peptides of different affinities were used to compete for binding of 10 nM fluorescently labeled MBP to 100 nM DR2. Competitor peptides tested were MBP (85–99) (red open squares) as well as single amino acid analogues with substitutions at key DR2 anchor residues: alanine substitution of position 89 (green triangles), alanine substitution of position 92 (dark blue triangles), or aspartic acid substitution of position 92 (light blue circles). D, Real-time analysis of DM-catalyzed and noncatalyzed peptide binding to DR2/CLIP. DR2/CLIP (100 nM) was incubated with labeled MBP peptide (10 nM) in the presence (blue line) or absence (black line) of DM (20 nM) at 25°C, and progression of the binding reaction was monitored by FP. As a control, DM (20 nM) and MBP peptide (10 nM) were incubated in the absence of DR2 (red line). E, A small molecule (M19) that significantly accelerates DM-catalyzed peptide binding. Screening of libraries of small molecules using this assay yielded four compounds that substantially accelerate the peptide binding reaction. The kinetics of reactions involving DR2, DM, and MBP peptide were compared in the absence of M19 (blue line) and in the presence of M19 (orange, 10 μM; red, 50 μM). M19 had no effect on FP measurements for reactions involving only the peptide (labeled MBP alone ± M19; blue: no M19, orange: 10 μM M19, red: 50 μM M19). MBP peptide, DM, and DR were used at 10 nM, 20 nM, and 100 nM, respectively.