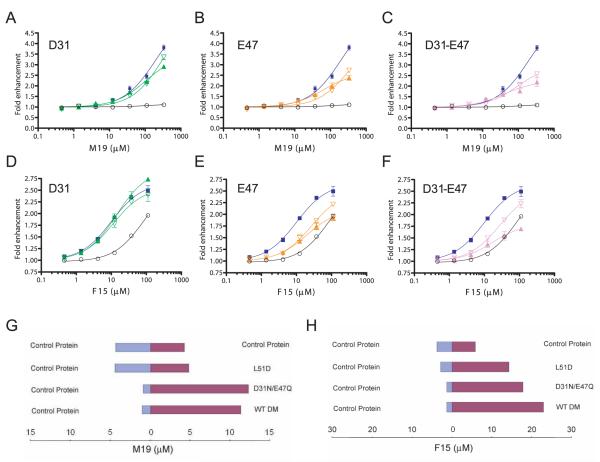
FIGURE 9.
Mutation of DM βE47 reduces the activity of M19 and F15. A–C, The dose response of M19 is shown for DM molecules with mutations at positions βD31 and/or βE47. Graphs show the M19 dose response with (A) βD31N (green, closed triangles) and βD31A (green, open triangles) (A); βE47Q (orange, closed triangles) and βE47A (orange, open triangles) (B), and E31N-βE47Q (purple, closed triangles) and βD31A-βE47A double mutations (purple, open triangles) (C). The dose response for reactions with wild-type DM (blue) and without DM (black) is shown in each graph. D–F, The corresponding experiments are shown for F15 with the set of mutants described in A–C. G, The βL51D mutation abrogates M19 binding, whereas the βD31N-βE47Q double mutation only affects activity. Microdialysis experiments were performed with wild-type DM and two DM mutants; the concentration of M19 in the two chambers was measured when equilibrium had been reached. H, Similar microdialysis experiments as described in G were performed with F15.