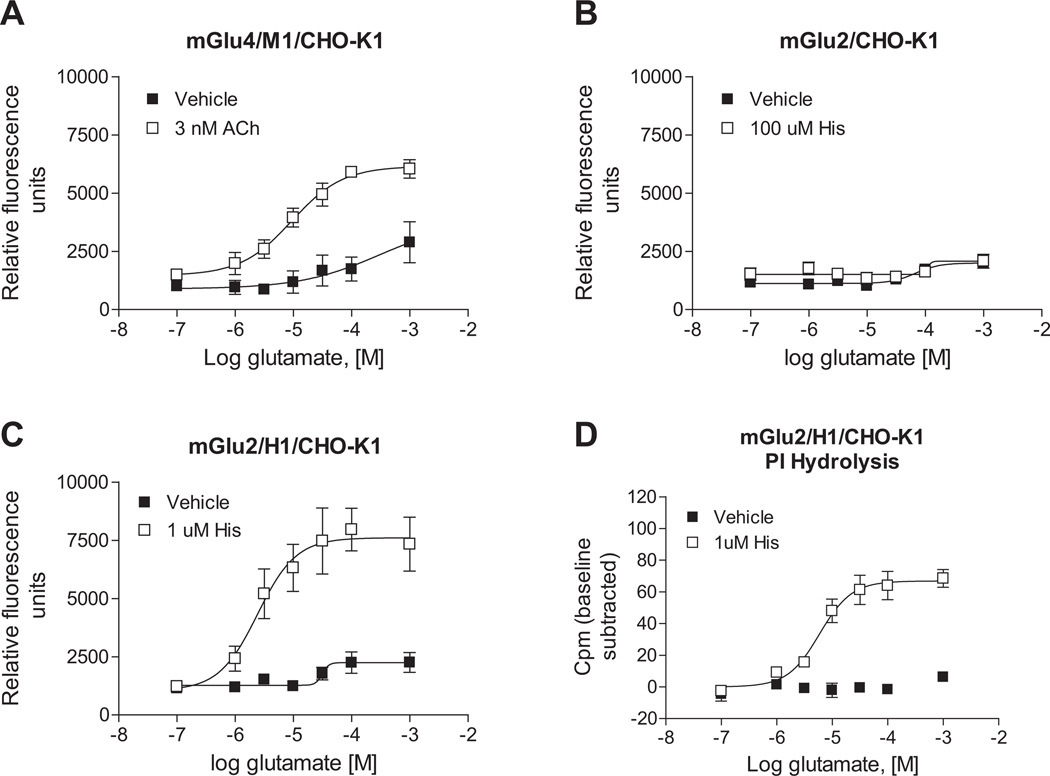
Fig. 5.
Phospholipase C pathway potentiation extends to additional Gq and Gi/o pairs. A, Acetylcholine (Ach) potentiates calcium responses induced by mGlu4 activation in mGlu4/M1/CHO-K1 cells. 3 nM Ach (□) or vehicle (■) control was added to cells in the first add, while increasing concentrations of glutamate were applied 150 s later in the second add and calcium mobilization was measured. Maximal responses in the absence or presence of 3 nM Ach were: 2889 ± 878 vs. 6175 ± 280 relative fluorescence units (*p = 0.024; unpaired t-test). Data shown were performed in triplicate; Mean ± SEM. B and C, histamine potentiates the calcium response of mGlu2 in the presence of the histamine H1 receptor in mGlu2/H1/CHO-K1 cells. In mGlu2/CHO-K1 cells, maximal responses in the absence or presence of 100 µM histamine were: 2072 ± 23.7 vs. 2122 ± 272 relative fluorescence units (p = 0.86; unpaired t-test). In mGlu2/H1/CHO-K1 cells, maximal responses in the absence or presence of 1 µM histamine were: 2796 ± 285 vs. 8223 ± 1128 relative fluorescence units (*p = 0.010; unpaired t-test). Data shown were performed in triplicate; Mean ± SEM. D, Histamine potentiates mGlu2 responses in phosphoinositide hydrolysis assays in mGlu2/H1/CHO-K1 cells. Cells were treated with increasing concentrations of glutamate in the presence of 1 µM histamine (□) or vehicle control (■). After 1 h incubation at 37 °C, accumulated inositol phosphates were measured according to description in 2.4. Phosphoinositide hydrolysis assays. Maximal responses in the absence or presence of 1 µM histamine were: 6.9 ± 1.8 vs. 68.7 ± 5.8 cpm (*p = 0.0005; unpaired t-test). Data from triplicate experiments are shown (Mean ± SEM) with relative baseline responses subtracted from each group. All Statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism (La Jolla, CA).