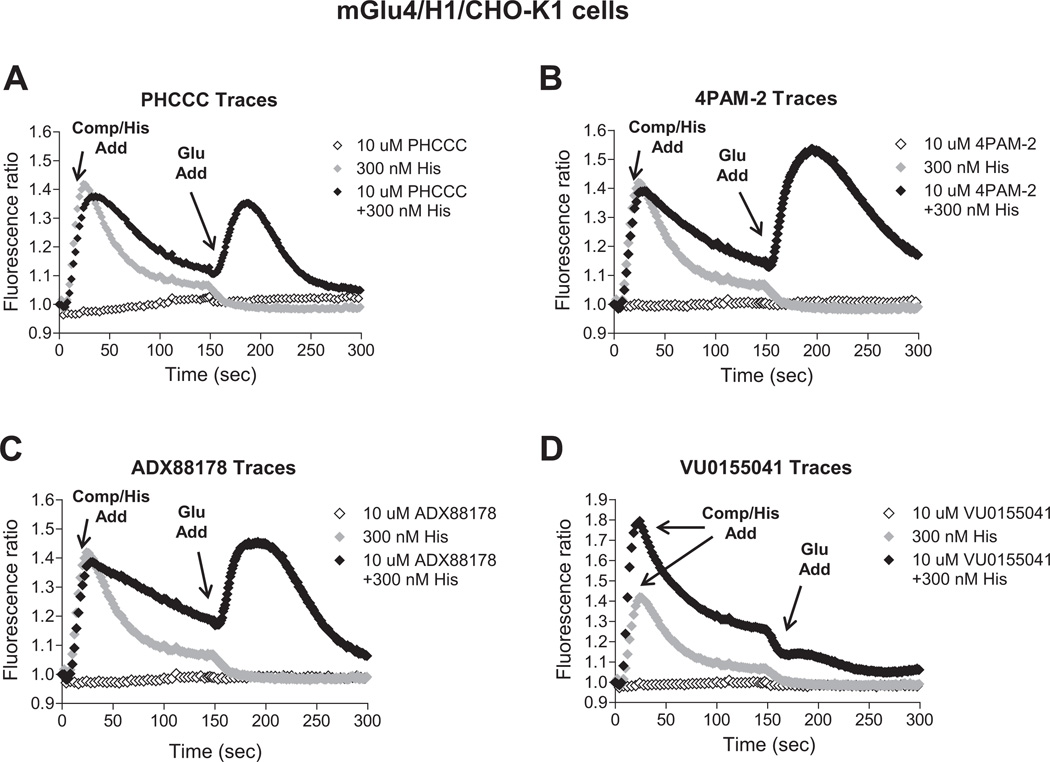
Fig. 7.
Histamine dramatically potentiates the effect of PAMs on mGlu4-mediated calcium mobilization in cells co-expressing mGlu4 and H1 receptors. Traces of calcium transients showing the effects of mGlu4 PAMs, histamine or the combination of both in potentiating the response of an EC20 concentration of glutamate (1 µM glutamate final) are shown. In these traces, a 10 µM concentration of each mGlu4 PAM (PHCCC, 4PAM-2, ADX88178 or VU0155041, in A-D respectively; (◇)), 300 nM histamine ( ) or combination of both (◆) were applied in the first add (“Compound/Histamine Add”). After 150 s, 1 µM glutamate (concentration determined based on cAMP experiments shown in Fig. 4A) was applied in the second add (“Glutamate Add”). Calcium responses were measured as the fluorescence ratio, which involves dividing all fluorescence data for each point in the kinetic trace by the fluorescence value obtained in the first baseline sample read, which corrects for differences in dye loading and cell plating.
) or combination of both (◆) were applied in the first add (“Compound/Histamine Add”). After 150 s, 1 µM glutamate (concentration determined based on cAMP experiments shown in Fig. 4A) was applied in the second add (“Glutamate Add”). Calcium responses were measured as the fluorescence ratio, which involves dividing all fluorescence data for each point in the kinetic trace by the fluorescence value obtained in the first baseline sample read, which corrects for differences in dye loading and cell plating.