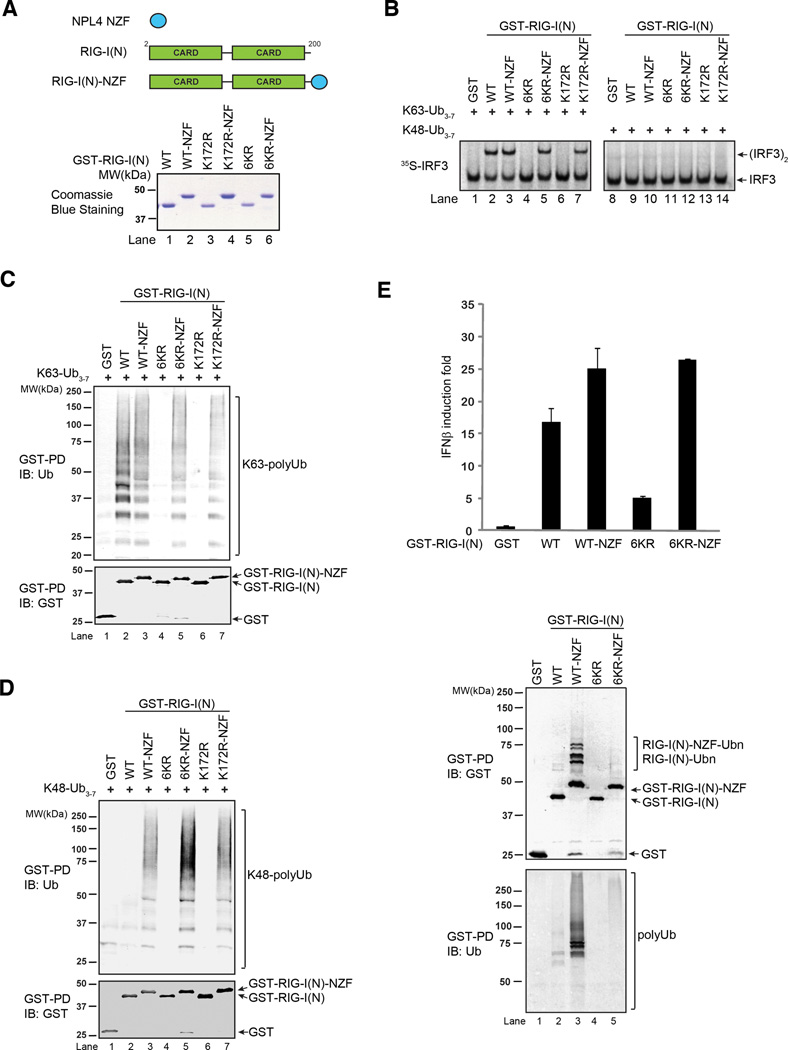
Figure 4.
Rescue of ubiquitination-defective mutants of RIG-I with a heterologous ubiquitin-binding domain. A. Diagram depicting the NPL4 novel zinc finger (NZF) ubiquitin binding domain and its fusion to RIG-I(N). The bottom panel shows GST-RIG-I(N) mutants and the NZF fusion proteins. B. Indicated proteins were incubated with K63- or K48-ubiquitin chains, and then analyzed for their ability to activate IRF3 dimerization in vitro. C & D. GST-RIG-I(N) mutant proteins were incubated with K63- (C) or K48- (D) linked ubiquitin chains followed by GST pull-down assays. E. RIG-I(N)-NZF fusion rescues the ability of 6KR to activate IFNβ reporter in vivo. Expression vectors for indicated proteins were transfected into HEK293T cells with IFNβ-luciferase reporter. Cell lysates were assayed for luciferase activity (top) or pulled down with glutathione Sepharose followed by immunoblotting (bottom). Results shown are representatives of two experiments.