Figure 3.
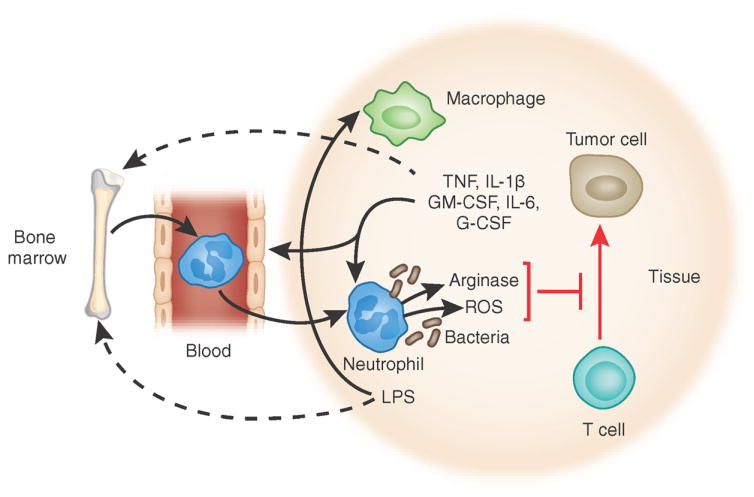
Features shared by ‘neutrophil MDSCs’ and neutrophils in mice with polymicrobial infection. Growth factors and cytokines generated by tumors and macrophages, as well as bacterial products, modulate the development and phenotype of neutrophils by acting both on developing neutrophils in the bone marrow and locally on neutrophils in tissues. Mast cells (not shown here) also can generate many cytokines and growth factors that can influence neutrophils, including TNF, IL-1β, GM-CSF and IL-6. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and arginase secreted from activated neutrophils can inhibit T cell function and permit tumor growth. In this setting, such neutrophils constitute ‘neutrophil MDSCs’. LPS, lipopolysaccharide.
