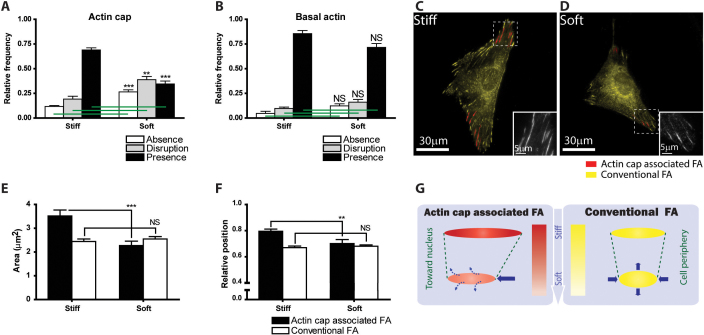
Figure 5. Differential response of actin cap and actin cap associated focal adhesions to changes in substrate compliance.
(A) and (B) Proportion of cells showing a well-organized (black), disorganized (grey), or no (white) actin cap (A) and basal actin stress fibers (B) on stiff and soft substrates. (C) and (D) Representative organization and number of actin cap associated focal adhesions (red) and conventional focal adhesions (yellow) in WT cells placed on stiff (C) and soft substrate (D). Insets, details of (unlabeled) focal adhesions in control cell. (E) and (F) Changes in average surface area (E) and relative position between the periphery (1) and the center (0) of the cell (F) of actin cap associated focal adhesions (black bars) and conventional focal adhesions (white bars) in response to changes in substrate compliance. (G) Schematic of the differential regulation of size, shape, length, breadth, and position of actin cap associated focal adhesions and conventional focal adhesions by substrate compliance (also based on data in Fig. S2, S4, and S5). In panels A and B, at least 300 cells were analyzed for each condition and repeated 5 times in WT control and 3 times in the other conditions; In panels E and F, at least 300 focal adhesions were analyzed for each condition; ***: P < 0.001; **: P< 0.01; NS: P > 0.05.