Figure 1.
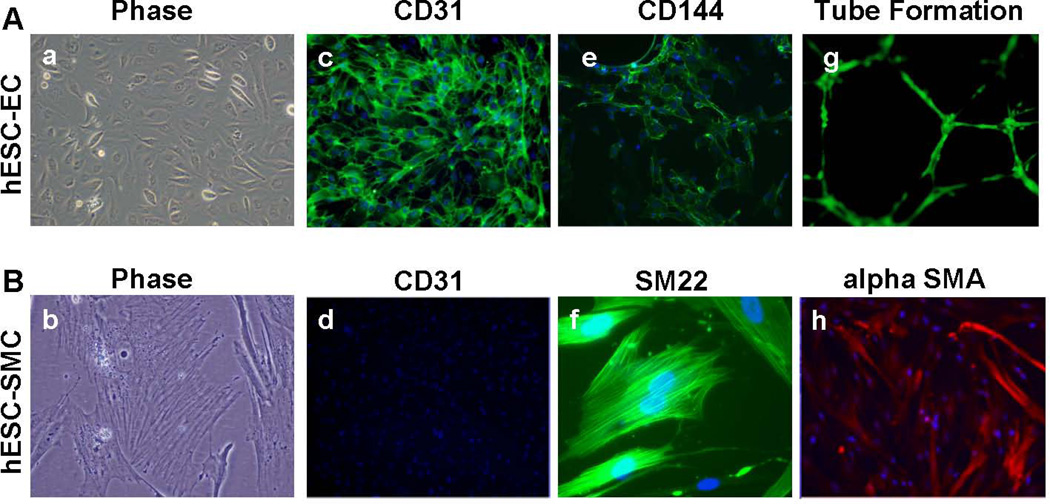
Endothelial and Smooth Muscle Cells Derived from Human Embryonic Stem Cells.
Using GFP/Luc expressing H9 human embryonic stem cells, distinct populations of endothelial and smooth muscle cells were derived from a common CD34+CD31+ vascular progenitor cell population. Panel A (left to right) hESC-ECs showed classic cobblestone morphology, expressed CD31 (PECAM), CD144 (VE-Cadherin), and formed capillary structures on Matrigel. Original magnification: 40×. Panel B (left to right) hESC-SMCs assumed appropriate filamentous morphology, lacked expression of endothelial marker CD31, and expressed smooth muscle makers SM22 and alpha-smooth muscle actin (alpha SMA). Original magnification: 40× (alpha-smooth muscle actin, CD31) and 80× (phase, SM22). Panel a–f and h were acquired from GFP− cells to avoid overlapping of immunofluorescence (Alexa Fluor 488) and GFP expression.