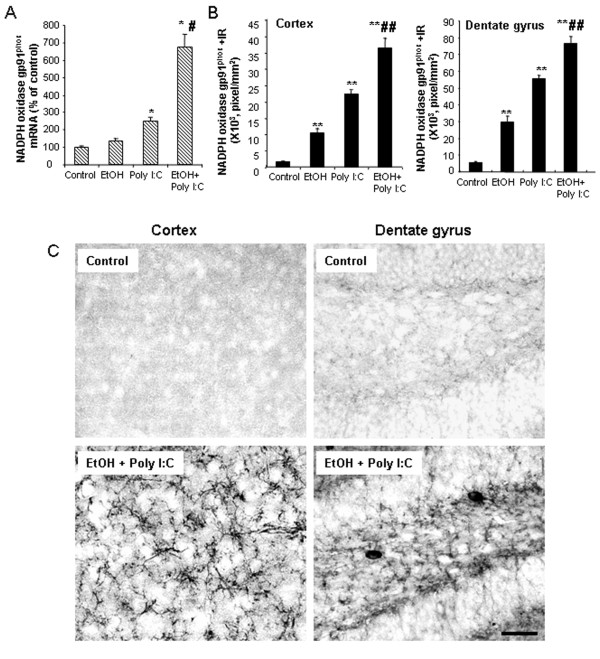
Figure 5.
Induction of NOX-NADPH oxidase subunit gp91phoxexpression. Male C57BL/6 mice were treated with ethanol, poly I:C, ethanol-poly I:C as indicated in methods. (A) gp91phox gene expression was determined by real-time PCR three hours after poly I:C treatment. Note chronic ethanol pretreatment increased brain poly I:C-induced gp91phox mRNA by 2.7-fold. (B) NADPH oxidase subunit gp91phox + IR in cortex and dentate gyrus (DG). Sections were stained with monoclonal mouse gp91phox antibody and quantified by BioQuant image analysis system. NADPH oxidase subunit gp91phox + IR was increased in cortex about 6 fold by ethanol and 14 fold by poly I:C and in DG about 5 fold by ethanol and 10 fold by poly I:C. Pretreatment of ethanol significantly enhanced poly I:C-induced gp91phox + IR in both cortex and DG. (C) The images shown are representative of gp91phox + IR cells from cortex (left) and dentate gyrus (right) for control (upper images) and ethanol-poly I:C groups (lower images). *P <0.05, **P <0.01, compared with the vehicle control mice. #P <0.05, ##P <0.01, compared with poly I:C-treated mice. Scale bar, 200 μm.