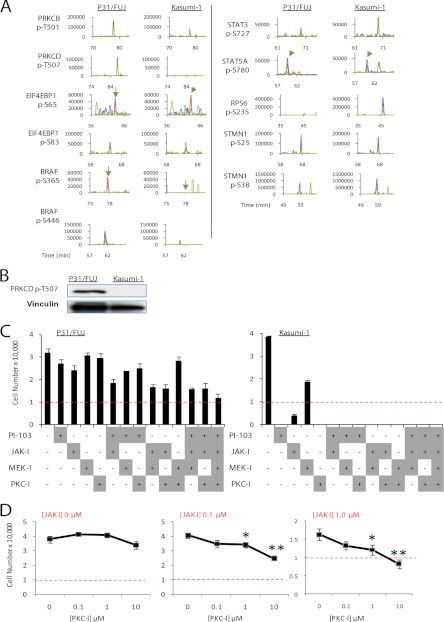
Fig. 7.
Kinase pathways cooperate to drive the proliferation of multidrug-resistant cells. A, XICs of peptides in P31/FUJ and Kasumi-1 bearing phosphorylation sites markers of pathway activation. Signals for the first, second, and third isotopes are depicted in blue, red, and green, respectively. Vertical arrows indicate the position of the named phosphopeptide in the chromatogram. B, Western blot of Thr(P)-507 PRKCD. C, proliferation of cells exposed to different combinations of kinase inhibitors. Inhibitor treatment was for 48 h at 100 nm (PI-103), 1 μm (JAK-I), 10 μm (MEK-I), or 10 μm (PKC-I). The initial number of cells seeded was 10,000 (indicated with a red dotted line). The data points are the means ± S.E. (n = 5). D, proliferation of P31/FUJ cells exposed to different combinations of JAK-I and PKC-I showing that these inhibitors potentiate each other in inhibiting cell viability. Note that combination of 1 μm JAK-I with 10 μm PKC-I resulted in a lower number of cells compared with input, indicative of cell death. The data points are the means ± S.E. (n = 5). *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.