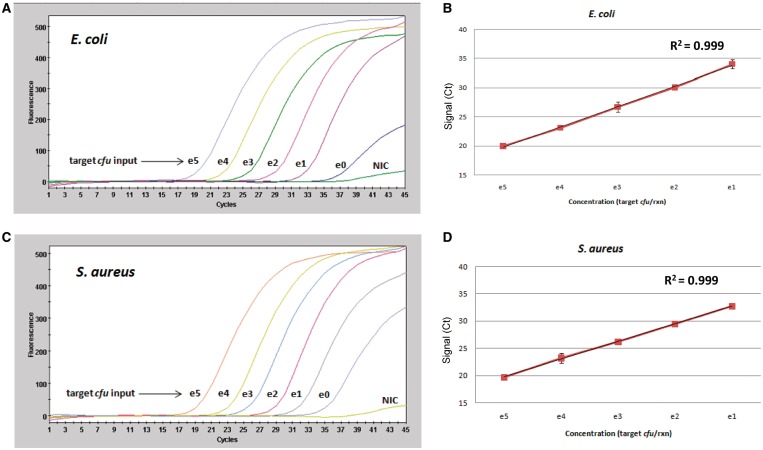
Figure 4.
DPE-PCR enables sensitive and quantitative detection of Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria via measurement of DPE activity in crude lysates. (A) Decreasing amounts of E. coli colony forming unit were spiked into bead lysis-coupled DPE-PCR. NIC were also included to monitor reagent background levels. All colony forming unit spikes and NICs were performed in triplicate. A representative DPE-PCR curve is shown below for each level of bacterial input. Colony count plating and gsPCR were performed in an effort to obtain a better estimate of the actual colony forming unit placed into each reaction and is presented in Supplementary Figure S5 (B) A plot of E. coli DNA polymerase activity and linear regression analysis is presented. Graphs were generated using the average Ct values obtained from triplicate reactions of bacterial spikes ranging from 1 × 105 to 1 × 101 input colony forming unit. (C and D) Colony forming unit titration experiments were performed for S. aureus exactly as described above for E. coli. Colony count plating and gsPCR were performed in an effort to obtain a better estimate of the actual colony forming unit placed into each reaction and is presented in Supplementary Figure S6.