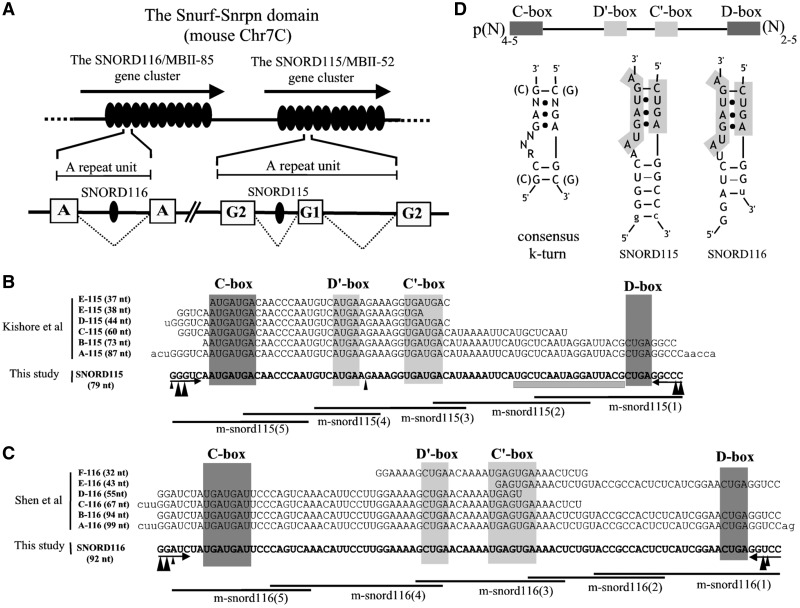
Figure 1.
A complex array of tandemly repeated C/D snoRNA genes mapping at the imprinted Prader–Willi Syndrome (PWS) locus. (A) Schematic representation of the two major arrays of repeated C/D snoRNA genes mapping at the mouse Snurf–Snrpn locus: the SNORD115 and SNORD116 genes [formerly known as MBII-52 and MBII-85, respectively (20)]. C/D snoRNA sequences (symbolized as black ovals) are embedded within repeated introns of long non-protein-coding RNAs comprising repeated exons (white rectangles, G2- and G1-exons for SNORD115 and A-exons for SNORD116). (B) Sequences of full-length mouse SNORD115 (A-115 form) and related psnoRNA species (E-115, D-115, C-115 and B-115 forms) as reported by Kishore et al. (31). The sequence of mouse SNORD115 as originally predicted (20) and used in this study is written in bold characters, with small vertical black arrowheads positioning the 5′ and 3′ extremities determined experimentally. Note that the sequence of the A-form., as well as the D-form, contains additional nucleotides from the surrounding intronic sequences (lower-case letters). The C/D and C′/D′ boxes are highlighted in dark and light grey, respectively, while the canonical (4–5 bp) terminal stem is indicated by inverted small horizontal arrows. The conserved antisense element matching the serotonin receptor (5-HT2C) mRNA is underlined by a horizontal grey bar. The relative positions of DNA oligonucleotides used in this study are also shown below the sequence alignments. (C) Sequences of full-length mouse SNORD116 (A-116 form) and related psnoRNA species (F-116, E-116, D-116, C-116 and B-116 forms) as reported by Shen et al. (30). Legends are as in panel (B). The sequence of the A-116 form considered by Shen et al. (30), as well as the C-116 form, contain additional nucleotides from the surrounding intronic sequences (lower-case letters). Note that the mouse SNORD116 RNA sequence, as originally reported in (20) and written here in bold characters, was edited at 2 nt positions (+7 and +69) to fit with the currently available mouse SNORD116 genomic sequences. (D) Top: Schematic representation of the consensus structure of mammalian box C/D snoRNAs (6). Left: Schematic representation of a consensus K-turn motif (7). SNORD115 (middle) and SNORD116 (right) display canonical 5′–3′-terminal stem structures that bring together the (C) and (D) boxes (highlighted in grey) that form part of the K-turn motif.