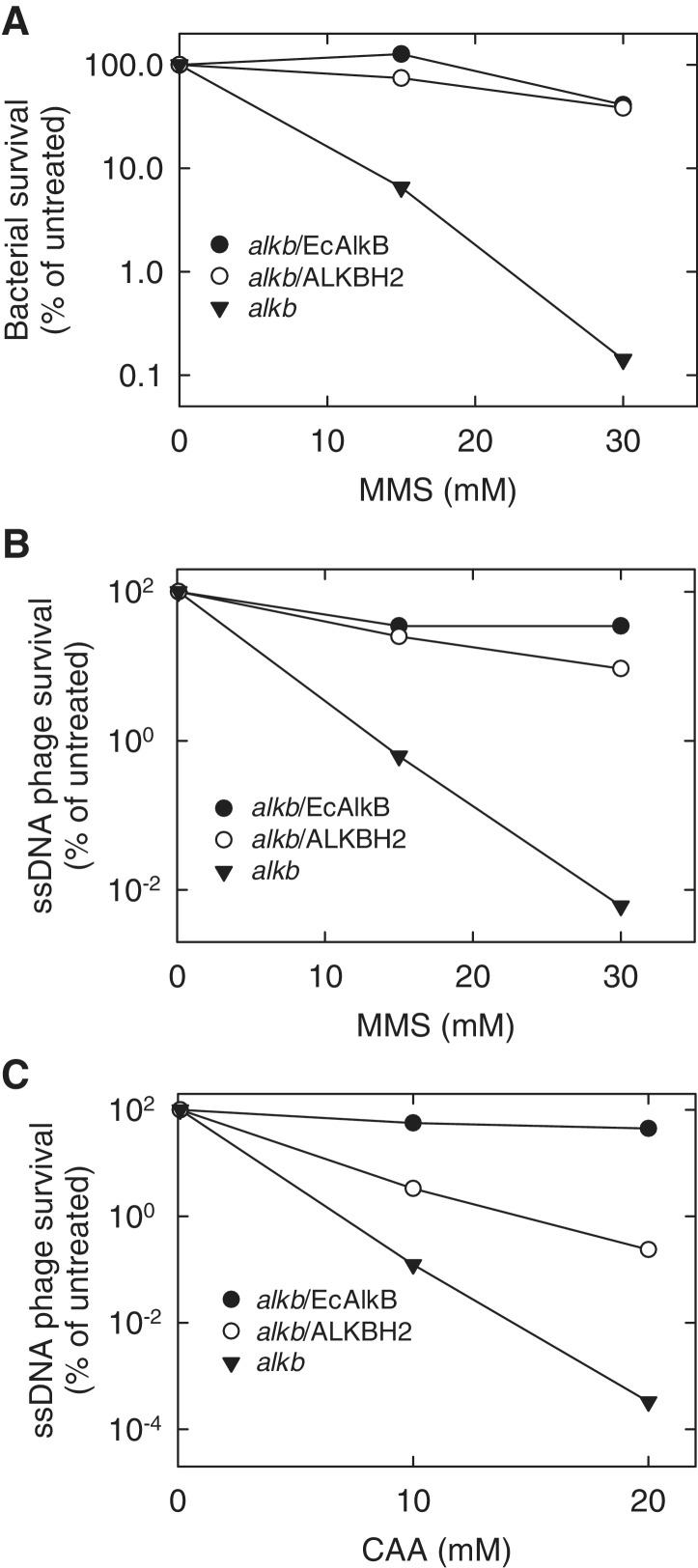
Figure 2.
Arabidopsis ALKBH2-mediated repair of DNA damage in the E. coli alkb mutant. EcAlkB-expressing plasmid and empty expression plasmid were included as positive and negative control, respectively. (A) Complementation of the MMS sensitive phenotype of E. coli alkB mutant bacteria by plasmid-expressed ALKBH2. The bacteria were treated with the indicated concentrations of MMS, plated out on agar plates, and the survival was assessed by colony counting. (B) Ability of ALKBH2 to increase the survival of methylated ssDNA phage. Phage M13 was treated with the indicated concentrations of MMS and mixed with alkb E. coli expressing the indicated proteins. Top agar was then added to the mixture, which was plated out on agar plates. Phage survival was scored by counting resulting plaques. (C) ALKBH2-mediated survival of CAA-treated ssDNA phage. Identical experiment to that in (B), except that CAA was used instead of MMS.