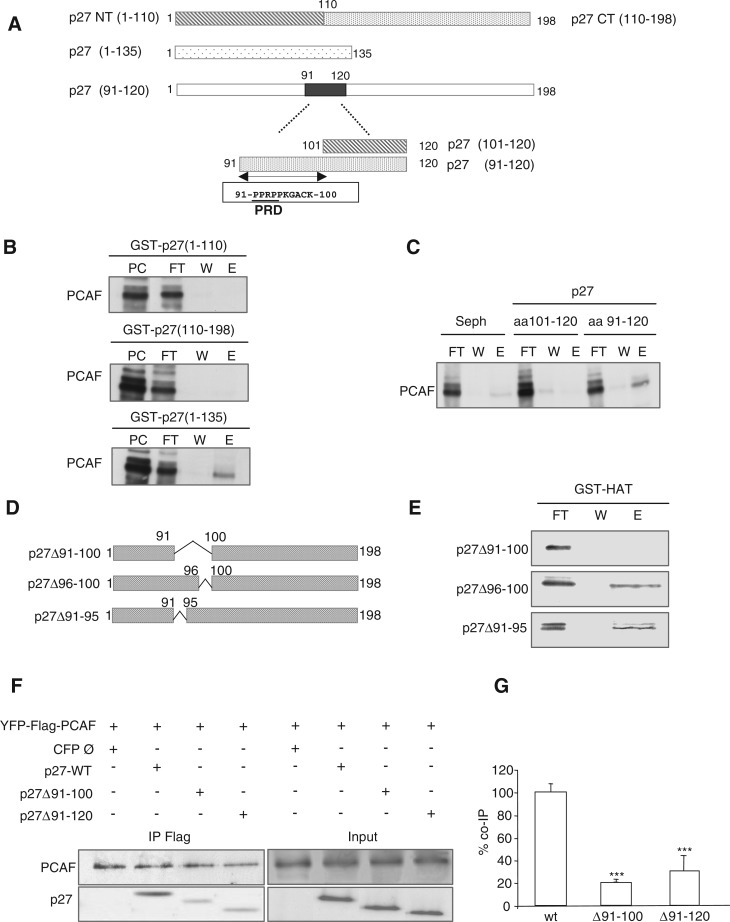
Figure 2.
The PID of p27 includes amino acids 91–120. (A) Graphic showing different fragments and domains of p27 used in the experiments. (B) Purified PCAF was loaded on GST–p27(1–110), GST–p27(110–198) and GST–p27(1–135) affinity chromatography columns. Then, the input (PC), the flow trough (FT), the last wash (W) and the eluate (E) fractions were subjected to electrophoresis and visualized by WB. (C) Purified PCAF was loaded on p27(101–120) and p27(91–120) affinity chromatography columns. As a control a Sepharose 4B column (Seph.) was used. Then, the flow trough (FT), the last wash (W) and the eluate (E) fractions were subjected to electrophoresis and visualized by WB. (D) Graphic showing the three p27 deletion mutants used in the experiments. (E) Purified p27(Δ91–100), p27(Δ96–100) and p27(Δ91–95) proteins were loaded on a GST–HAT column. Then, the flow trough (FT), the last wash (W) and the eluate (E) fractions were subjected to electrophoresis and visualized by WB. (F) HEK293T cells were transfected with YFP–Flag–PCAF plus p27WT or plus the deletion mutants p27(Δ91-100) or p27(Δ91–120) or woth an empty CFP vector (Ø). Then, cell extracts were subjected to IP with anti-Flag and the immunoprecipitates analyzed by WB with anti-p27 and anti-PCAF. (G) Experiment in (F) was repeated three times and quantified. Results were expressed as the mean value ± SD. Statistical analyses were performed using Student's two-tailed paired t-test. Values of P < 0.05 were considered statistically significant. ***P < 0.001.