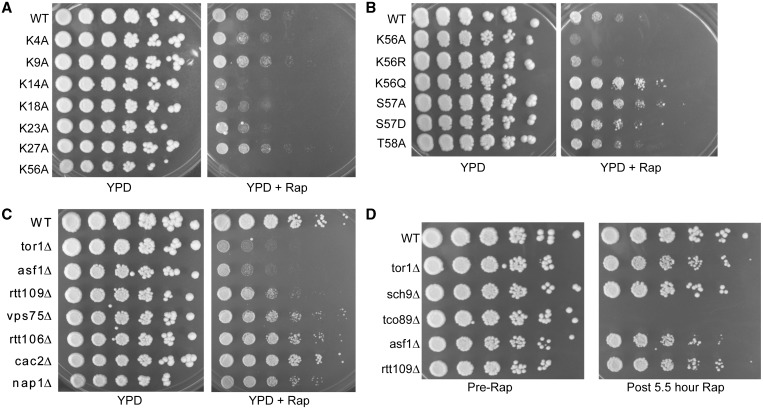
Figure 1.
The H3K56ac pathway is required for TORC1-regulated growth. (A) H3 lysine to alanine mutants exhibit variable sensitivity to rapamycin. Wild-type (WT) and the indicated histone H3 lysine to alanine mutants were grown overnight at 30°C and then cell density for each strain was measured by taking the OD600. Equivalent numbers of cells were serially diluted 5-fold and replica spotted to control YPD or YPD plates containing 25 nM rapamycin and incubated at 30°C for 4 days before photographing. (B) Acetylation of H3K56 is key in TORC1-regulated growth. Experiment was performed as in (A) except photographs were taken at 3 days to highlight the growth difference between the H3K56Q and WT strains. (C) H3K56ac regulators are selectively required for TORC1-dependent cell growth. The experiment was performed as in (A) with the WT and indicated gene deletion mutants. Photographs were taken after 4 days at 30°C. (D) H3K56ac regulators do not undergo cell-cycle arrest after an inhibitory rapamycin treatment. The indicated yeast strains were cultured to log phase and then equal numbers of cells were pelleted, 5-fold serially diluted and spotted to YPD plates. The remaining cultures were treated with 200 nM rapamycin for 5.5 h and then equal numbers of cells were pelleted, washed and 5-fold serially diluted before spotting to YPD plates. Photographs were taken after incubation at 30°C for 3 days.