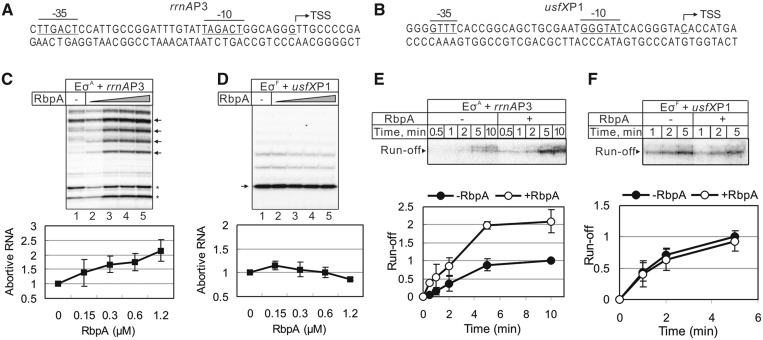
Figure 1.
Effects of RbpA on σA and σF dependent transcription. (A and B): Sequences of the rrnAP3 and usfXP1 promoters. The −10 and −35 consensus elements are underlined, and transcription start sites (TSS) are marked by arrows. (C and D) Abortive transcription carried out by the σA-containing RNAP (EσA) on the rrnAP3 template and σF-containing RNAP (EσF) on the usfXP1 template. Lanes 2–5: RbpA was added to 0.15, 0.3, 0.6 and 1.2 µM, respectively. Quantification of the bands indicated by arrows is shown on the bottom graphs. The RNA amounts were normalized to the value obtained without RbpA (lane 1). The error bars are the SD of triplicate experiments. (E and F) Kinetics of single-round run-off transcription carried out by σA-containing RNAP on the rrnAP3 and by σF-containing RNAP on the usfXP1 template, respectively. RbpA (1.2 μM) was added to the reaction when indicated. The quantification of the run-off RNA is shown on the bottom graphs. The RNA amounts were normalized to the amount of RNA synthesized without RbpA after 10 min of transcription (rrnAP3) or 5 min of transcription (usfXP1). The error bars are the SD of duplicate experiments.