Fig. 4.
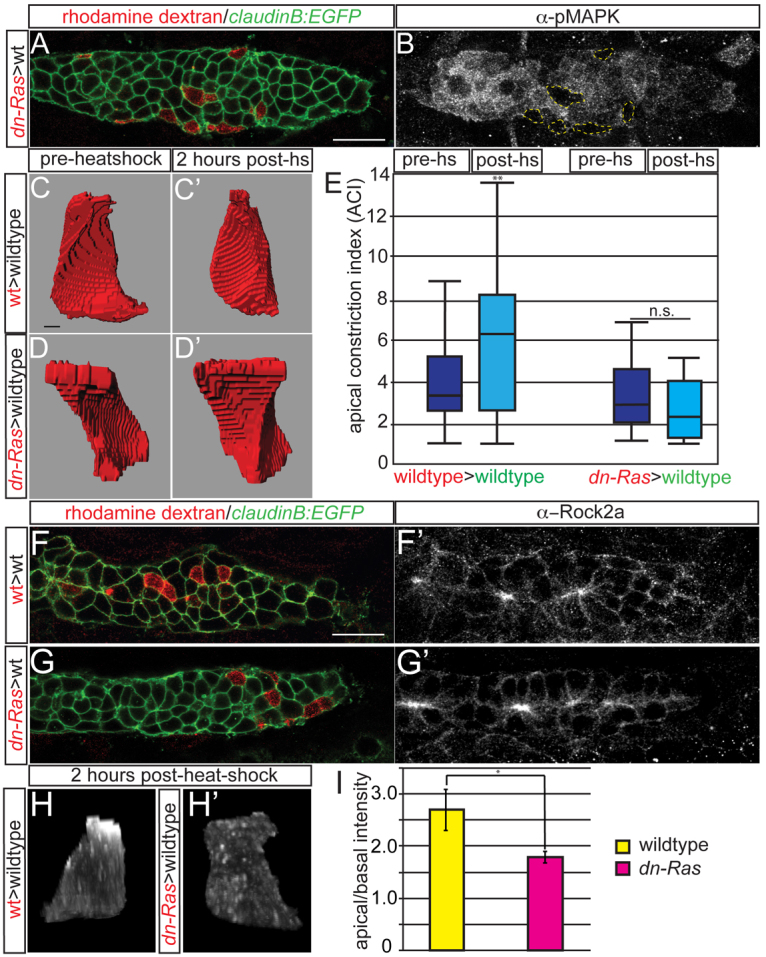
Ras-MAPK signaling mediates cell-autonomous apical constriction and Rock2a localization. (A,B) claudinB:EGFP-positive mosaic zebrafish embryos containing hsp70:dn-Ras donor cells (red) at 30 hpf. Note the lack of pMAPK labeling in dn-Ras cells. (C-D′) Before heat shock, both dn-Ras and wild-type donor cells are columnar; 2 hours after heat shock, the wild-type cell is constricted, whereas the dn-Ras cell remains columnar. (E) Quantification of ACIs of transplanted wild-type and hsp70:dn-Ras cells before and after heat shock. n=50 cells from ten embryos. **P<0.009, Wilcoxon test. n.s., not significant. (F-G′) Transplantation of hsp70:dn-Ras or wild-type cells causes no obvious differences in global Rock2a distribution. (H,H′) Rock2a distribution in a single transplanted cell shows failure of Rock2a apical localization when Ras is inhibited. (I) Ratio of apical to basal fluorescence intensity in transplanted wild-type cells and dn-Ras cells. n=15 cells from four embryos per condition. *P<0.03, ANOVA. Error bars indicate s.e.m. Scale bars: 20 μm in A,F; 2 μm in C.
