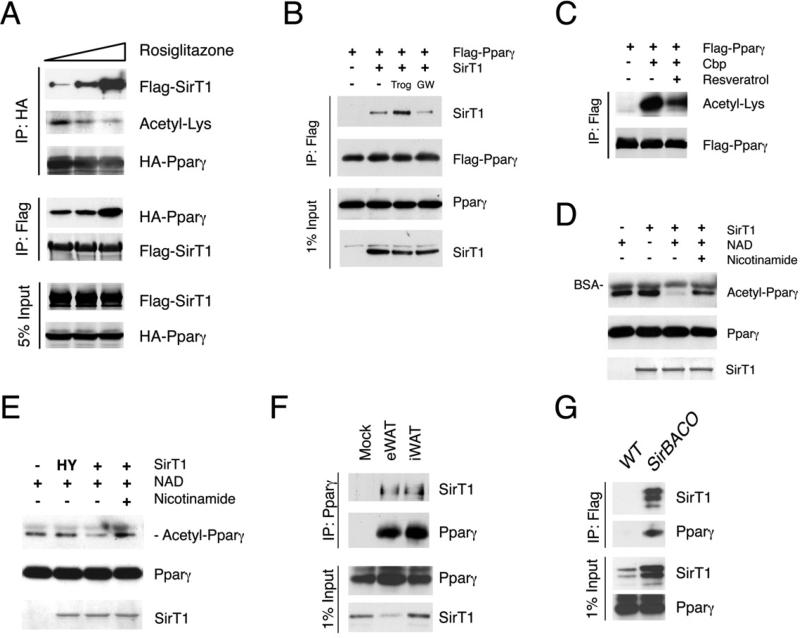
Figure 1. SirT1 deacetylates Pparγ in a ligand-dependent manner.
(A) Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) of Flag-tagged SirT1 or HA-tagged Pparγ in response to overnight rosiglitazone treatment in 293 cells.
(B) Co-IP of Flag-Pparγ and SirT1 in 293 cells treated with troglitazone (Trog) or GW9662 (GW) overnight.
(C) Pparγ acetylation in 293 cells in response to resveratrol.
(D-E) In vitro Pparγ deacetylation by SirT1. Bovine serum albumin (BSA) is contained in the reaction buffer.
(F) Co-IP of Pparγ with SirT1 in mouse adipose tissues. We immunoprecipitated 2 mg of epididymal (eWAT) or inguinal fat lysates (iWAT) with Pparγ antibody H100, and blotted the immunoprecipitates with SirT1 or Pparγ (E8) antibodies.
(G) Co-IP of SirT1 and Pparγ with Flag M2 beads using iWAT (5 mg) from SirBACO mice expressing Flag-tagged SirT1.
See also Figure S1.