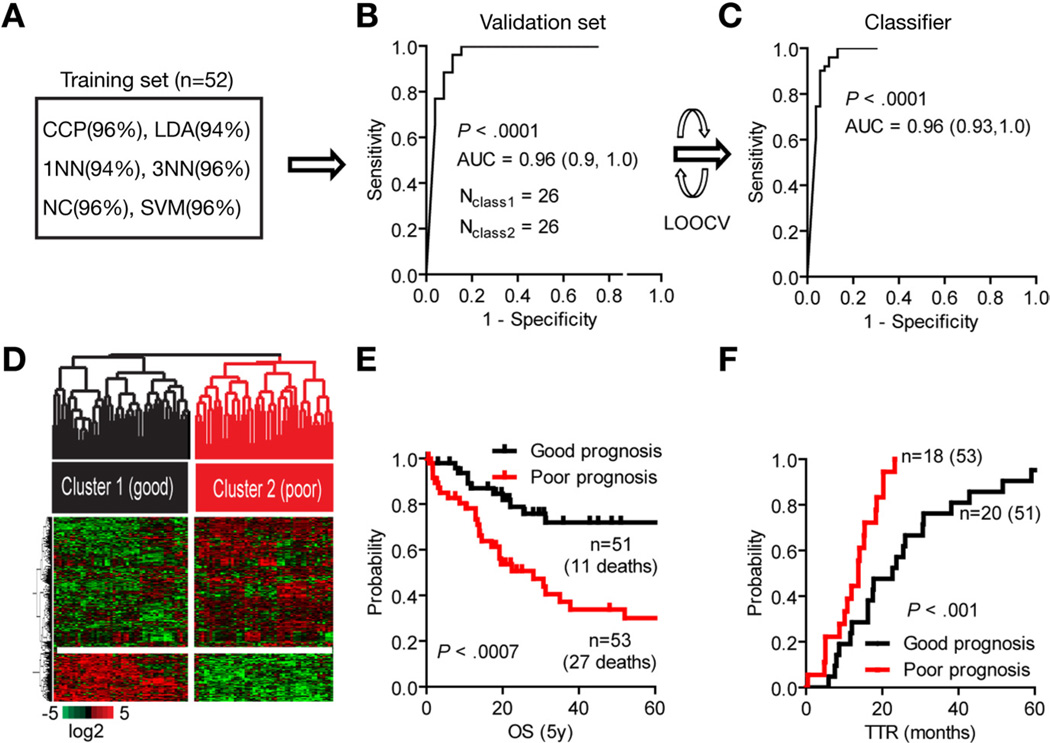
Figure 1.
Development of a CCA gene classifier. (A) Multiple class comparison models were used to test the robustness of the classification in the training set (n = 52). (B) Sensitivity of the gene signature to correctly predict the classification of patients within the validation set (n = 52). The specificity is represented by the area under the receiver and operator curve (AUC, 95% CI) using Bayesian compound covariate predictor modeling. (C) Development of the gene classifier. To build the classifier, a class random variance model was used, identifying 238 genes significant at α ≤ .001 using Bayesian compound covariate modeling and leave-one-out cross-validation (LOOCV). (D) Hierarchical clustering of the 238-gene classifier separates patients into 2 subclasses according to their clinical outcome. (E) Analysis of survival (OS) and (F) time to recurrence (TTR). Kaplan–Meier and log-rank statistics were used to determine levels of significance.