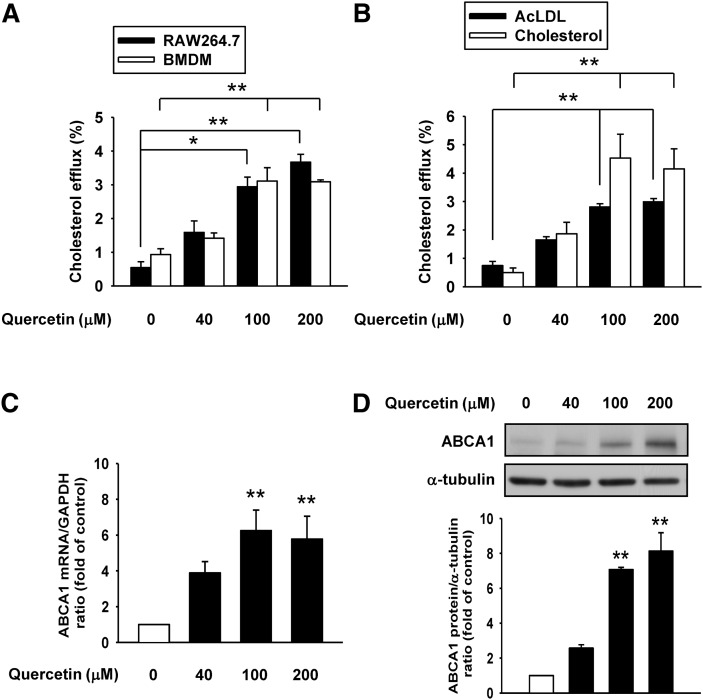
Fig. 1.
Quercetin enhances cholesterol efflux and expression of ABCA1 in macrophages. A: [3H]cholesterol-labeled RAW264.7 macrophages or BMDM were treated with quercetin as indicated concentrations for 24 h. ApoAI-dependent cholesterol efflux was measured by incubating [3H]cholesterol-labeled macrophages with or without 10 μg/ml apoAI for 24 h. Cholesterol efflux was expressed as the percentage of radioactivity in the medium relative to the total radioactivity (medium and cells). B: RAW264.7 macrophages were loaded with 10 μg/ml of acetylated low-density lipoprotein (AcLDL) or 30 μg/ml cholesterol in the presence of [3H]cholesterol for 24 h. Cholesterol efflux was measured as described in Materials and Methods. C: After cells were treated with quercetin for 18 h, mRNA levels of ABCA1 were detected by quantitative real-time PCR and normalized to GAPDH. D: Cells were treated with quercetin for 24 h, and then total cell extracts were harvested. ABCA1 protein expressions were measured by Western blot analysis and α-tubulin was utilized as a loading control. The normalized level of mRNA or protein from cells without quercetin treatment was set as 1. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 3–5). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 versus control group.