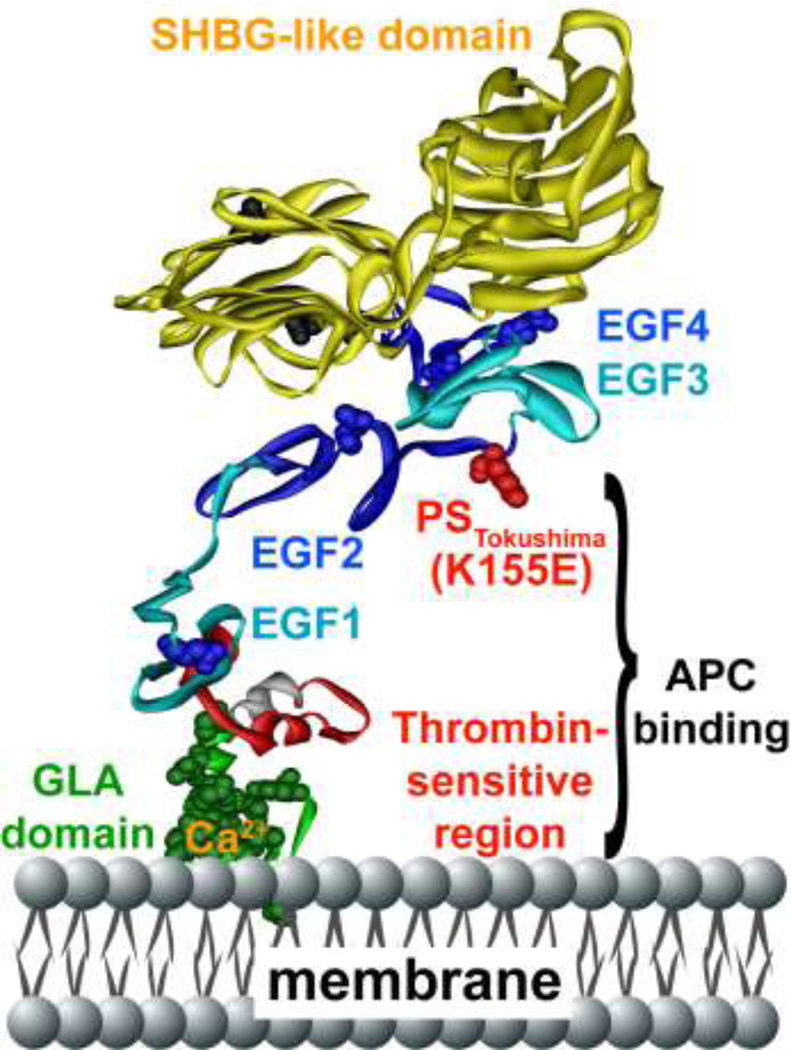
Figure 2. Protein S polypeptide scheme showing multiple domains and protein S Tokushima mutation.
Specific protein S domains are color coded and labeled. The N-terminal cluster of domains is responsible for binding to APC. The amino acid side chain of residue 155 is shown in red, representing the protein S Tokushima polymorphism, K155E (“155” is the mature protein S numbering which equates to K196E in full length precursor numbering). The schematic model of protein S was based on available models and structures of the individual GLA-TSR-EGF1 [167], EGF3–4 (1Z6C) [168], and the SHBG [169] domains. EGF2 was modeled by homology modeling using Swiss Model based on templates for extracellular domain of the LDL receptor (1N7DA), low-density lipoprotein receptor (1HZ8A), low-density lipoprotein receptor (1HJ7A) and EGF-like module-containing mucin-like hormone receptor-like 2 (2BO2A) as templates [170]. The individual domains were put together using Modeller [171], displayed and colored in Accelrys Discovery Studio and rendered in POV-Ray.