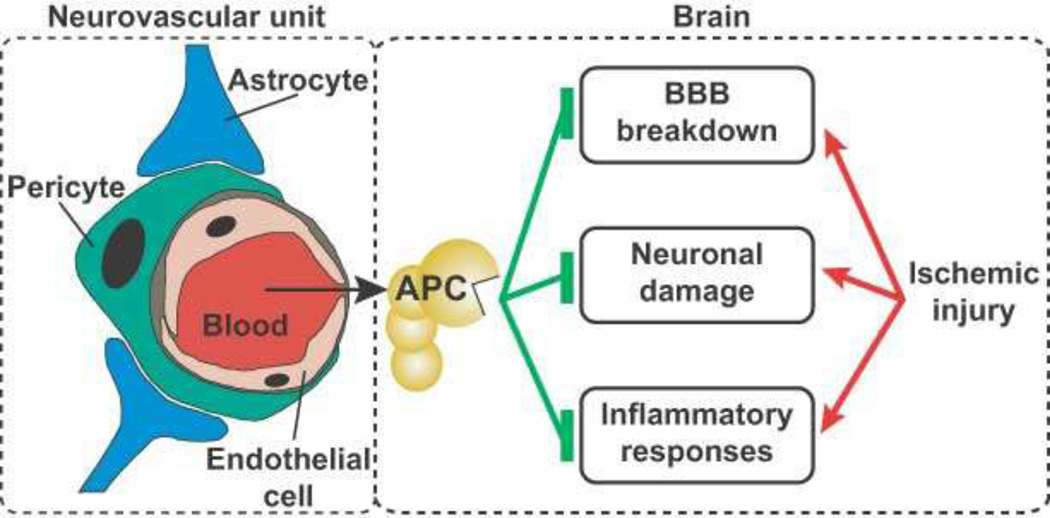
Figure 4. APC’s neuroprotective actions on the neurovascular unit following ischemic injury.
Ischemia promotes endothelial cell apoptosis, breakdown of the blood-brain-barrier (BBB), neuroinflammation, and damage to neurons. By its cytoprotective actions, APC protects vascular integrity and ameliorates post-ischemic BBB breakdown, thereby preventing secondary neuronal damage mediated by entry of several blood-derived neurotoxic and vasculotoxic molecules. APC can cross an intact BBB via EPCR-dependent transport to reach its neuronal targets in brain. APC can express direct neuronal protective activity to prevent neuron damage. APC also expresses anti-inflammatory activities by blocking early post-ischemic infiltration of brain by neutrophils and by suppressing microglia activation.