Fig. 10.
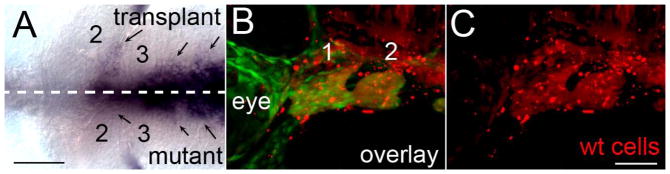
A Hh-dependent relay from neural crest to the endoderm regulates shha expression. fli1:EGFP;smo−/− embryos received transplants of neural crest cells from fli1:EGFP;smo+/+ donors. The fli1:EGFP;smo+/+ donors were injected with Alexa 568 dextran to visualize the transplanted cells (in red). (A) Ventral view of a 36 hpf smo mutant labeled with a riboprobes against shha showing more extensive shh expression on the side receiving the transplant (arrows). The dashed line marks the midline of the embryo as determined by the position of the notochord and ventral diencephalon. (B & C) Lateral view of the same embryo in A, imaged previously at 30 hpf, demonstrating contribution of wild-type neural crest cells to the pharyngeal arches. (B) shows the overlay of fli1:EGFP expression and Alexa 568 dextran fluorescence while (C) shows just the dextran fluorescence. The first two pharyngeal arches are numbered, anterior is to the left in all images. Scale bar=50μm.