Figure 3. Changes in mean ± SD cycle duration, peak amplitude, burst duration and burst area established on the basis of EMG recordings from soleus (Sol) and tibialis anterior (TA) muscles of both hindlimbs during locomotion in the horizontal and upright postures in different experimental conditions.
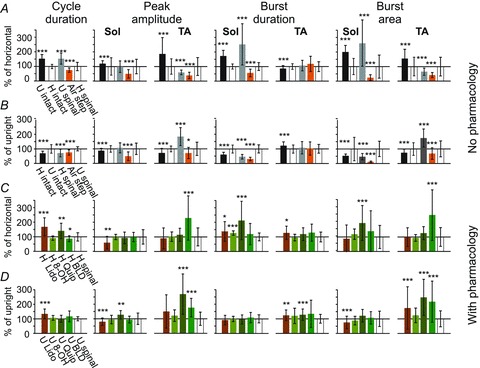
Each bar is the mean of 4–6 spinal rats and 5 experiments from intact rats taken from 10–30 consecutive steps in both hindlimbs during rhythmic movements in a particular experimental condition. The means in A are expressed as the percentage of that obtained during locomotor trials in the horizontal posture. The means in B are expressed as the percentage of the values obtained during trials in the upright posture. 100% represents the mean value obtained in the control situation for each analysed index (white bar). The black bar on the left represents results obtained during locomotor trials of intact rats in the upright posture in comparison to the horizontal posture (A) and in the horizontal posture in comparison to the upright posture (B). For example, in the case of the cycle duration index, the mean cycle duration of intact rats in the upright posture is longer than that obtained during locomotor trials in the horizontal posture. Similarly, the grey bars represent the means obtained in spinal rats, showing that the cycle duration increases significantly when going from the horizontal to the upright posture (A), and decreases when going from upright to the horizontal posture (B). The orange bar represents the means of each index for air-stepping. C and D, pharmacological treatments induce different effects on locomotor movements recorded in the horizontal and upright postures. The values after treatment are expressed as a percentage of the values measured from locomotor trials taken before the pharmacological treatment. Abbreviations: U, upright posture; H, horizontal posture; air step, air-stepping; Quip, quipazine (0.1–0.25 mg kg−1i.p.); 8-OH, 8-OH-DPAT (0.1–0.4 mg kg−1i.p.); Lido, lidocaine injections into the hindpaw bilaterally (0.05 ml, one medial and one lateral in each paw); BLD, both Quip and 8-OH-DPAT, low dose (0.1 mg kg−1). Wilcoxon's non-parametric test: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.02, ***P < 0.01.
