Figure 5. Anaesthesia of plantar surface of the paw eliminates plantar stepping produced by tail pinching in the upright posture.
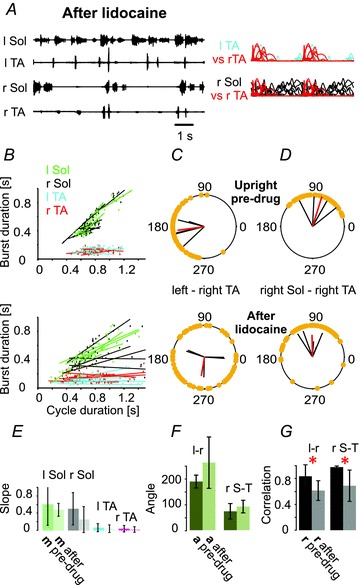
A–D, lidocaine (n = 4) disrupts locomotion in the upright posture (A–C), as shown in EMG recordings (A) and by the alteration in the burst duration–cycle duration relationship (B and E), as well as the disruption of inter- (C) and intra-limb (D) coordination (upper panels, pre-drug; lower panels, after lidocaine application). F and G, bar graphs showing the mean angle of polar plots (a, ±SD) for the left–right TA (l-r) and for the right Sol–right TA (r S-T) relationships and the mean of correlation coefficients (r, ±SD) for the left–right TA (l-r) and for the right Sol–right TA (r S-T) relationships, indicating a highly significant decrease in r for inter- and intralimb coordination in the upright posture trials after lidocaine application. The remainder of this figure is as described in the Fig. 1 legend.
