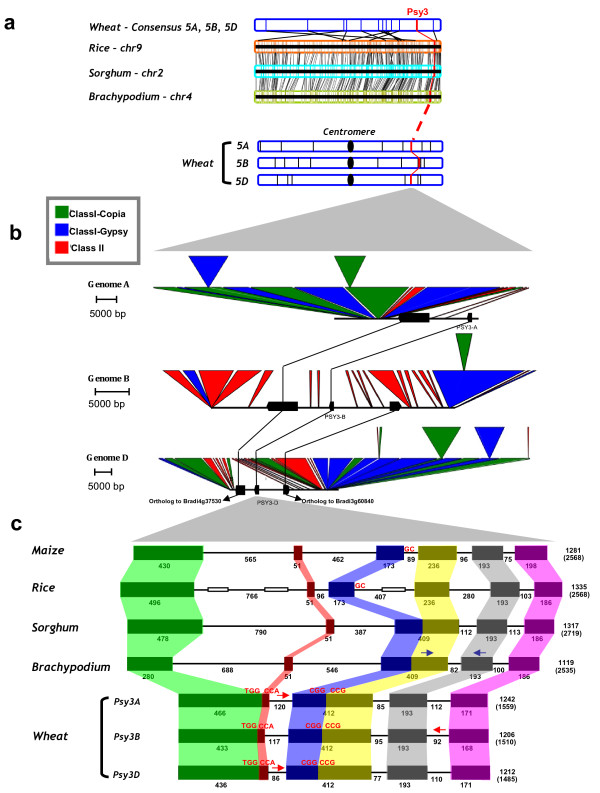
Figure 2.
PSY3 gene characterization in bread wheat. (a) The physical position of wheat PSY3 on chromosome group 5 and associated deletion bin are shown. Vertical bars on wheat chromosomes represent chromosome bins. The orthologous chromosomes in rice (Chr9), sorghum (Chr2) and Brachypodium (Chr4) are illustrated by conserved genes linked with black lines. (b) Annotated BAC clones are illustrated by conserved genes (black boxes) linked with black lines as well as Copia (in green), Gypsy (in blue) and class II (in red) transposable elements. (c) Comparison of PSY3 gene structures in Grasses (maize, rice, sorghum, Brachypodium and wheat) is shown based on coloured boxes highlighting conserved exons. Intron and exon sizes are shown as well as the total gene (in brackets) and CDS sizes. Maize and rice PSY3 share the same structure with six exons of conserved sizes and five introns. Their third intron shows a difference in size but in both rice and maize its 5′ starts with the same GC motif (highlighted in red), instead of GT. Sorghum and Brachypodium PSY3 show a structure of five exons and four introns. Wheat PSY3 have lost two introns probably due to the illegitimate recombination between the inversed repeated motives, TGG|CCA and CGG|CCG, identified at the deletion breakpoints (highlighted in red). White boxes represent MITEs identified on rice PSY3 sequence. Blue arrows show the position of primers designed on Brachypodium PSY3 sequence and used for BAC library screening. Red arrows correspond to specific primers, designed on intron sequence and used to assign BAC clones to A, B and D sub-genomes in wheat