Figure 1. Up and Down states and Up-and-Down transitions in two different network models.
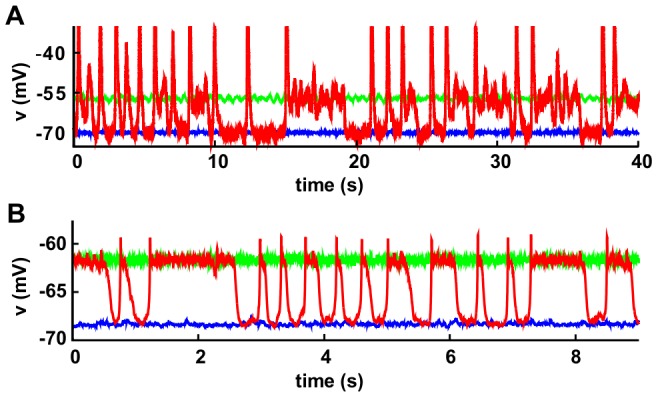
(A) Model A (mean-field model) [18]: time-series for the membrane potential, 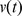 . Observe the presence of two steady states lower one around
. Observe the presence of two steady states lower one around 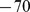 mV (Down-state/blue curve) and a larger one (Up state/green curve) at about
mV (Down-state/blue curve) and a larger one (Up state/green curve) at about 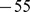 mV; these two are obtained for low noise amplitudes (
mV; these two are obtained for low noise amplitudes (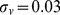 mV
mV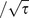 ,
, 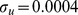
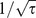 ) and different initial conditions. Instead, the Up-and-Down state (red curve), corresponds to a high noise amplitude (
) and different initial conditions. Instead, the Up-and-Down state (red curve), corresponds to a high noise amplitude (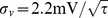 ,
, 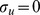 ). Note that, typically the Up-state intervals start with an abrupt spike which parallels empirical observations as discussed in [18]. Parameters have been fixed as in [18]:
). Note that, typically the Up-state intervals start with an abrupt spike which parallels empirical observations as discussed in [18]. Parameters have been fixed as in [18]: 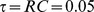 s,
s, 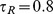 s,
s, 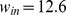 mV/Hz,
mV/Hz, 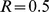 ,
,  mV,
mV, 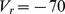 mV, and
mV, and 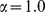 Hz/mV. (B) Model B (network of spiking neurons) [21]: Time series of membrane potential. Curves and color code are as for Model A. For
Hz/mV. (B) Model B (network of spiking neurons) [21]: Time series of membrane potential. Curves and color code are as for Model A. For 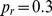 the system exhibits Up-and-Down transitions, for larger (smaller) values as
the system exhibits Up-and-Down transitions, for larger (smaller) values as 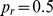 (
(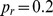 ), it remains steadily in the Up (Down) state. Parameters have been fixed as in [21]: vesicles per synapsis
), it remains steadily in the Up (Down) state. Parameters have been fixed as in [21]: vesicles per synapsis 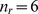 , resting potential
, resting potential 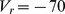 mV, membrane threshold
mV, membrane threshold  mV, capacitance
mV, capacitance 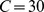 pF, leakage characteristic time
pF, leakage characteristic time 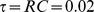 s, synaptic recovery time
s, synaptic recovery time 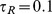 s, signal time decay
s, signal time decay 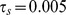 s, refractory period
s, refractory period 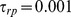 s, input amplitudes
s, input amplitudes 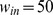 pA,
pA, 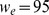 pA, and external driving rate
pA, and external driving rate 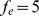 Hz.
Hz.
