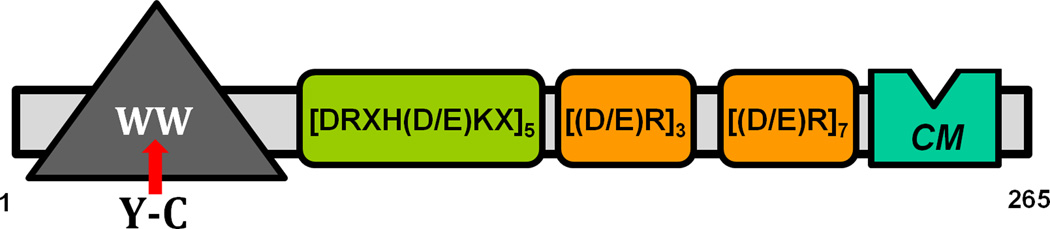
Figure 1.
Schematic of the organization of the PQBP1 protein. PQBP1 contains only one discernable modular domain, the WW domain located at the N-(amino)-terminus. The causative Y-C PQBP1 mutation of the GIH syndrome is located within the middle of the WW domain sequence and it is indicated with a red arrow. There are multiple copies of three distinct amino acid repeats found in PQBP1: five consecutive copies of DRXH(D/E)KX and ten copies of (D/E)R, which occur consecutively in repeats of three and seven separated by a small stretch of intervening amino acids. At the C-(carboxy)-terminal region there is a stretch of highly conserved amino acids –GPLFQQRPYPSPG-, which are identical among PQBP1 proteins of man (Homo sapiens), a sweet water polyp (Hydra magnipapilata) and a small flowering plant (Arabidopsis thaliana). We indicate the relative location of this sequence as a green box with CM, after “conserved motif”. An indentation on the box is to suggest a possibility that the CM motif interacts with the WW domain, shown as a gray triangle.