Figure 5.
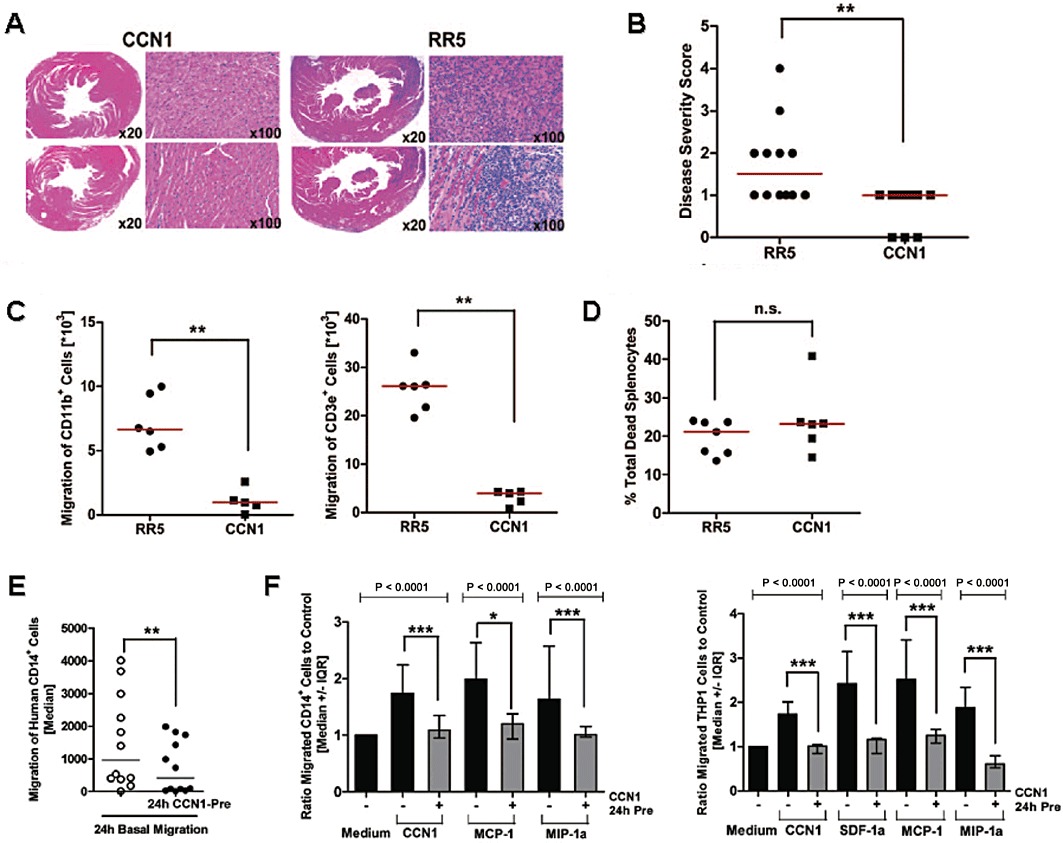
Systemic CCN1 therapy attenuates murine autoimmune cardiomyopathy (Rother et al. 2010) (reproduced by permission from Circulation). (A) Treatment with a CCN1 gene transfer vector (AdV-CCN1) significantly reduced cardiac immune cell infiltration as assessed by histological analysis of mouse hearts after 3 weeks, in comparison with RR5 control vector-treated animals. (B) The cardiac disease score was significantly reduced by this treatment. (C) Migration assays of splenocytes isolated from mice at peak inflammation showed significantly reduced ex vivo migration of CD11b+ macrophages (left) and CD3e+ T cells (right) from AdV-CCN1-treated mice compared with controls. (D) No difference in cell viability was detected. (E) Mechanistic studies of CCN1 effects in vitro showed a significantly reduced basal migration rate of human CD14+ monocytes. (F) Abrogation of the chemotactic response to chemokines (SDF-1α, MCP-1. MIP-1α) important in the pathogenesis of diverse cardiovascular and inflammatory diseases. SFD-1α, stromal cell-derived factor-1α; MIP-1α.
