Figure 4.
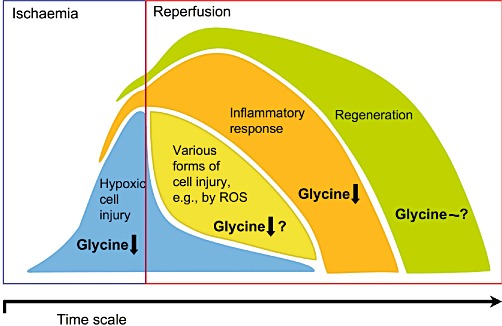
Cell injury, inflammatory response and regeneration during or following ischaemia–reperfusion. Protective effects of glycine. At concentrations around 1 mM and above, glycine decreases hypoxic cell injury by direct cytoprotection and inhibits the inflammatory response. A direct cytoprotective effect of glycine on other forms of cell injury occurring during reperfusion, such as those mediated by ROS, remains a matter of debate. The mechanism of protection by glycine at low-dose treatment regimens is unknown. The same is true for the effect of glycine on regeneration of the tissue injured by ischaemia–reperfusion.
